基金项目:苏州国际快速物流通道二期工程-春申湖路快速化改造工程(CSH-TJ05)
作者简介:薛青松(1986-),男,学士,工程师,主要从事隧道工程的设计和管理工作。E-mail:354677901@qq.com
通信作者:林永亮(1977-),男,博士,主要从事岩土工程等方面的研究。E-mail:lin_yliang@163.com
1.中铁二十局集团第一工程有限公司,江苏 苏州 215151;2.上海大学力学与工程科学学院,上海 200444
1.China Railway 20th Bureau Group First Engineering Co.,Ltd.,Suzhou 215151, China;2.School of Mechanics and Engineering Sciences , Shanghai University , Shanghai 200444, China
Diaphragm wall; Silty sand layer; Artesian water; Limit equilibrium; Safety factor of stability
DOI: 10.13512/j.hndz.2022.01.16
随着城市地下空间的不断开发利用,作为深基坑围护结构的地下连续墙也具有广泛的运用前景,尽管地连墙成槽施工中积累了丰富的经验,但在成槽土体开挖中依然面临槽壁塌孔或塌槽问题,尤其承压水作用下粉砂层土体开挖时,槽壁极易发生失局部塌孔,根据以往工程施工经验,槽壁失稳既有整体失稳,也有局部失稳,这些都会对后续地连墙施工产生很大影响,进而影响最终成墙质量。因此,针对承压水作用下粉砂层失稳模式和机理分析就显得十分必要。
槽壁失稳破坏问题一直是地下连续墙施工中亟待解决的技术难题,为此,国内外学者也对槽壁失稳进行了大量的理论分析,Britto等[1]假定了7种成槽开挖的失稳模式,并给出其相应的解析解。姜朋明等[2]基于极限分析理论对地连墙成槽施工中的时间效应进行了深入分析。张厚美等[3]假定槽壁破坏体为倾斜滑动抛物线柱体,为了确定最危险破坏面对滑动体进行三维理论分析。王轩等[4]结合现有的槽壁整体稳定性分析方法,从理论基础的角度对槽壁影响参数进行敏感性分析,并结合实际效果进行验证分析。丁勇春等[5]针对成槽施工中的槽壁失稳现象,采用理论分析的方法对不同施工阶段下的槽壁土体的应力路径进行研究。陈孟红[6]提出土体破坏平面速度场模型,采用极限分析上限理论对槽壁土体进行分析。Han等[7-8]针对黏性土层中槽壁局部破坏模式,建立了二维和三维破坏模型对该土层的局部稳定性进行了极限理论分析。易岸峰[9]建立了富水地层中槽壁稳定性分析模型,依据极限平衡原理推导出成槽施工中槽壁整体稳定性最小护壁泥浆的计算公式。崔根群等[10]分别建立了地连墙整体和局部稳定性力学模型,采用极限平衡法推导出了保证槽壁稳定的护壁泥浆重度临界值计算公式。周洋[11]依托苏州轨道交通5号线地连墙为工程背景,利用整体和局部失稳理论解对成槽开挖中槽壁稳定性进行分析。刘杨等[12]针对富水软弱地层建立了局部失稳力学模型,对模型进行极限平衡分析,推出槽壁局部失稳极限支护压力和最低泥浆液面高度。欧明喜等[13]采用朗肯极限平衡原理对黏土夹砂层局部稳定性进行分析,推出槽壁局部稳定性系数计算公式。
目前,针对复杂地层下地连墙开挖槽壁失稳进行了大量的理论分析,但对于承压水作用下粉砂层槽壁失稳机理就鲜有研究,因此,基于实际工程中粉砂层整层失稳模式进行计算假定,采用极限平衡分析方法,通过建立槽壁失稳三维分析模型,提出承压水作用下粉砂层槽壁稳定性安全系数计算方法,并结合工程声波实测进行对比验算,在工程实例的基础上对槽壁稳定性主要影响因素进行参数敏感性分析,可为后续类似粉砂地层地连墙施工提供些许理论参考。
地连墙成槽施工是个动态的过程,地连墙在成槽施工中经常发生失稳破坏,当土层中存在粉砂层且含有承压水时,土体极容易发生局部失稳,整个破坏过程往往可分为三个阶段,首先是成槽土体开挖导致粉砂层土体出现局部剥落,由此进入槽壁失稳破坏的第一阶段,从而呈现出小范围的局部失稳。随着静置时间的增加,槽壁破坏区域继续扩大,继而进入槽壁失稳破坏的第二阶段,破坏区域范围会进一步扩大,进而导致整个粉土夹砂层出现整层滑动破坏,即为粉砂层整层失稳破坏。之后,粉砂层整层失稳破坏会不断延伸至上覆土体,进而导致上部土体出现失稳破坏,失稳破坏的范围持续增大,最终进入槽壁失稳破坏的第三阶段,槽壁土层会出现跨多层大范围的整体失稳破坏。而在实际地连墙施工中,槽壁失稳破坏的第三阶段的破坏形状可分为两种形态,一种是当粉砂层的上覆土层厚度较浅时,粉砂层整层失稳区域会沿着上覆土层一直延伸至地表,从而槽壁会呈现出滑动体沿着地表发生整体滑动失稳,如图1所示。另一种形态是当粉砂层的上覆土层厚度较深时,粉砂层整层失稳区域会沿着上覆土层延伸至上覆土一定范围内,而不会延伸至地表,槽壁从而会出现滑动体沿着上覆土层一定深度范围内发生整体滑动失稳,如图2所示。
图1 延伸至地表整体失稳Fig.1 Overall instability of the overlying surface
图2 延伸至上覆土层整体失稳Fig.2 Overall instability of the overlying soil layer
图3为苏州春申湖路快速化改造工程中湖区地连墙局部失稳破坏的超声波检测图,图中显示槽壁局部失稳出现在粉土夹砂层,破坏区形状呈现楔形体滑动破坏。失稳破坏区域位于⑥3粉土夹砂层,且该土层存在一定水头高度的承压水,从而导致该土层出现局部失稳,而④2粉土夹砂层含有微承压水却没有发生局部失稳破坏是由于在湖区槽段在成槽施工前采取了减压降水措施,降低了④2粉土夹砂层的微承压水头高度,因此,该土层超声波检测图显示槽壁较为平整,无明显失稳破坏。由此得出,粉土夹砂层在承压水的作用下槽壁容易发生局部失稳破坏,且破坏区域形状表现为楔形滑动体沿着某个滑裂面出现滑动破坏。
图3 湖区槽段超声波检测图Fig.3 Ultrasonic inspection of grooves in the lake area
地连墙施工需要穿越粉砂层,且粉砂层存在承压水时,使得护壁泥浆的压力不足以平衡侧向的土压力和水压力的合力,从而导致粉砂层槽壁出现局部失稳坍塌。本文依据上述工程中粉土夹砂层破坏形状从整层失稳破坏模式的角度对槽壁进行稳定性力学分析,一般认为粉砂层整层破坏为槽壁整体破坏的前提,考虑到地层中存在粉砂层且含有承压水的情况,滑动体破裂面形状一般为椭圆面,为了简化计算分析,假定粉砂层在承压水的作用下槽壁失稳破坏的形状为三角楔形滑动体,建立了粉砂层槽壁失稳破坏的剖面图,如图4所示。图中,粉砂层有效重度为γ'0,粉砂层厚度为d 0,泥浆重度为γs,泥浆高度为hs,地下水重度为γw,地下水高度为hw,承压水头高度为h 1。
图5为粉砂层槽壁失稳计算图示,滑动体ABCDEF高度为d0,滑动体长度为槽段长度L,滑动体滑裂面角度为θ,取θ=45° + φ'0/2。取图5失稳模型图中滑动体ABC进行受力分析,根据槽壁实际受力状态建立平面受力分析图,如图6所示。图6中,Q为附加荷载和上覆土层的合力,G为滑动体的自重,Ps为护壁泥浆压力的合力,Pw为地下水压力的合力,T1和N为滑动面ACDF上切向合力和法向合力,T2为滑动体两侧面ABC(DEF)上土体黏聚力合力。
图4 地连墙穿越粉砂层失稳破坏剖面图Fig.4 Instability failure profile of the diaphragm wall through silty sand layer
图5 地连墙槽壁失稳计算图示Fig.5 Calculation diagram of the instability of the trench wall of the diaphragm wall
滑动体ABCDEF的自重G为:
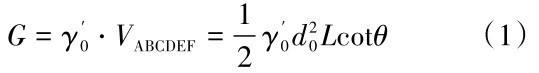
式中:γ'0为粉砂层的有效重度,VABCDEF为整个滑动体的体积。
作用在地面附加均布荷载为q,根据建筑基坑支护技术规程对地面附加荷载引起附加竖向应力标准值计算公式进行BCEF面上平均附加竖向应力的计算,从而求出地面附加荷载作用下在BCEF面上产生的合力,则作用在滑动体上的上覆土层的附加荷载合力Q为:
Q=( σ ave + γmd − γwhw )⋅Ld0 cotθ (2)
式中:σave为地面附加荷载引起的平均附加竖向应力,γm为上覆土层加权平均重度,γm =( γ1d1 +⋯+ γndn )/( d 1 + ⋯ + dn ), d为上覆土层的总厚度,d=d1 + ⋯ + dn。
图6 失稳模型受力分析图Fig.6 Force analysis diagram of the instability model
作用在滑动体上泥浆压力分布呈现梯形分布,如图7所示。则根据梯形面积公式可求出作用在滑动体上的泥浆压力合Ps为:
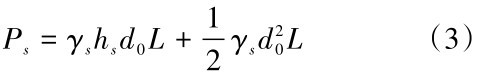
式中:γs为护壁泥浆的重度,hs为滑动体顶面至泥浆液面的高度。
图7 滑动体上泥浆压力和水压力分布图Fig.7 Mud pressure and water pressure distribution on sliding body
作用在滑动体上的地下水压力应包括潜水压力和承压水压力两部分,地下水压力分布如图7所示。则根据分布图可得出作用在滑动体上的地下水压力的合力Pw为:
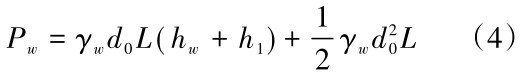
式中:γw为地下水的重度,hw为滑动体顶面至地下潜水面高度,h1为承压水头高度。
作用在滑动体滑裂面ACDF上的法向力合力N为:
N=( Q + G ) cosθ +( Ps − Pw ) sinθ (5)
作用在滑动体滑裂面ACDF的切向力合力T1为:
T1 =Ntanφ'0 + c'0SACDF=Ntanφ'0 + c'0d0Lcscθ (6)
式中:SACDF为滑裂面ACDF的面积,φ'0为粉砂层的有效内摩擦角,c'0为粉砂层的有效黏聚力。
作用在滑动体两侧面ABC(DEF)上黏聚力合力T2为:
T 2 =c'0 ( S ABC + S DEF )=c'0 d 20 cot θ (7)
式中:SABC和SDEF分别为侧面ABC和侧面DEF的面积。
为了考虑承压水作用下粉砂层地连墙成槽施工中的槽壁稳定性,引入槽壁稳定性安全系数,槽壁稳定性安全系数定义为滑动体的抗滑力与下滑力的比值,即:
Fs =Ts Tg(8)
式中:Ts为滑动体的抗滑力,Tg为滑动体的下滑力,按式(9)计算。
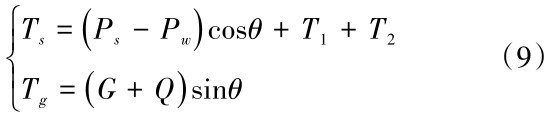
苏州春申湖5标段起于苏嘉杭高速东侧K9+830处,终点桩号K14+299.287,主线全长4.47 km,隧道采用围堰明挖法,基坑深度1.17~24.63 m,林家路处基坑最大深度24.63 m,湖中段基坑深度10.54~18.17 m,湖中基坑围护结构采用地下连续墙,地下连续墙主要为一字型,地连墙分幅槽段长度为6 m,墙厚为1 m,墙深度两侧导墙采用L型,现场地连墙施工如图8所示。
根据现场地质勘探,沿线场地地表下90.3 m深度范围内地基土构成除填土外,其余为第四系滨海、第四系河泛、河床相沉积物,一般由黏性土、粉(砂)土组成。场地浅层地下水中孔隙潜水主要赋存于浅部填土及黏性土中。场地微承压水主要赋存③3粉土及④2粉土夹粉砂中,其富水性一般,透水性较好,区内承压水主要赋存于⑥3粉土夹粉砂及⑦2粉土层中,富水性中等。
图8 现场地连墙成槽施工Fig.8 On-site construction of trenches with diaphragm walls
根据现场地质勘察,湖区地下潜水稳定标高在-2 m,微承压水主要存在于③3粉土及④2粉土夹砂层中,承压水最高水头标高为1.7 m。根据现场抓槽试验结果,④2粉土夹砂层粉砂性较重,且该层存在一定水头高度的微承压水,加剧槽壁的不稳定性,容易发生槽壁塌孔现象。在湖区K11+460附近进行试抓槽试验,湖区槽段的地质横剖面图如图9所示,土层物理力学参数见表1,成槽深度为15 m,塌孔范围主要在④2粉土夹砂层。
参照地质勘察情况,将湖区土层的参数信息代入上述推导的稳定性安全系数公式(8)和(9)。根据现场实际设计资料,相关土层及施工参数取值如下,地下水容重γw为10 kN/m3,地面附加荷载取20 kPa,现场实测泥浆重度γs为11 kN/m3,泥浆液面保持与导墙顶面齐平,粉土夹砂层的有效黏聚力c'0为3.2 kPa,有效内摩擦角φ'0为26.8o。当地下水未降水时,地下水位位于地面以下2 m,将上述参数信息代入本文推导的稳定性安全系数计算公式,得出Ts =1456.10 kN, Tg =1681.52 kN, Fs =0.87,地下水位位于地下2 m时,稳定性安全系数小于1,槽壁很可能会发生粉砂层局部失稳破坏。根据现场降水验证试验,采用井点降水来降低地下水位至地下4.5 m,且通过减压降水来降低承压水头,再次代入稳定性计算公式得出 Ts =2210.12 kN, Tg =2035.21 kN, Fs =1.09,稳定性安全系数明显提高,槽壁基本能保持粉砂层局部稳定性。为了验证理论计算的准确性,将理论计算结果和现场试抓槽试验进行对比分析。现场抓槽深度为15 m,图 10(a)为减压降水前抓槽试验超声波检测结果图,检测结果显示距地面10m左右出现塌孔,塌孔范围主要存在于④2粉土夹砂层,由此可得,现场声波实测结果和理论计算结果较为吻合。根据现场减压降水验证试验,采用井点降水来降低地下水位至地下-4.5 m,且同时对粉砂层采用减压降水来降低微承压水头,图 10(b)为减压降水后抓槽试验超声波检测结果图,由图可知,槽壁整体完整性较好,粉砂层无明显的塌孔现象。理论计算结果和现场试验较为吻合,从而验证了粉砂层稳定性理论计算公式的准确性。
图9 湖区槽段地质横剖面图Fig.9 Geological cross section of the lake area
为了探究承压水作用下粉砂层槽壁失稳主要影响因素的敏感性程度,本文基于上述工程实例基础上,采用上述的稳定性系数计算公式分别从承压水头、地下水位、泥浆液面、泥浆重度以及地面附加荷载对粉砂层槽壁稳定性影响因素进行参数分析。
图 10 现场抓槽试验超声波检测图Fig.10 Ultrasonic inspection diagram of on-site gripping test
图 11为槽壁稳定性安全系数随承压水头变化图,由图可知,承压水对粉砂层槽壁稳定影响很大,稳定性安全系数随承压水头的增大呈现直线减小趋势。经计算,当承压水头高度为0m时,稳定性安全系数为1.09,承压水头高度为6 m时,稳定性安全系数降至0.33,降幅达到69.7%。承压水头高度每增加1.5 m,稳定性安全系数会下降17.4%左右。因此,在承压水头较高的地层进行成槽开挖时,一定不能忽视承压水对粉砂层成槽开挖的影响,工程中尽可能在承压水头较低的季节施工,如遇工期紧急,在地连墙正式成槽施工前,应进行必要的减压降水措施,降低承压水头高度,从而避免粉砂层在高承压水头作用下发生局部失稳破坏。
图 11 稳定性安全系数随承压水头高度变化Fig.11 Variation of stability safety factor with the height of artesian water head
图 12为槽壁稳定性安全系数随地下水位深度变化图,由图可知,稳定性安全系数随地下水位深度呈曲线增长。经计算,当地下水位深度为0m时,稳定性安全系数为0.61,当地下水位降至地下6 m时,稳定性安全系数增至1.18,增幅达到93.4%。因此,对于湖区地连墙进行围堰施工,一定要采取必要的降水措施,降低槽壁两侧的地下水位至一定深度,才能保证粉土夹砂层在成槽施工中不会出现失稳破坏。
图 12 稳定性安全系数随地下水位深度变化Fig.12 Variation of stability safety factor with underground water level depth
图 13为槽壁稳定性安全系数随泥浆液面深度变化图,由图可知,泥浆液面对维持槽壁稳定起着至关重要的作用,随着泥浆液面的下降,槽壁稳定性安全系数会逐渐降低。经计算,当泥浆液面深度为0 m时,稳定性安全系数为1.09,当泥浆液面深度为2 m,稳定性安全系数降至0.81,降幅达到25.7%。实际上,随着地连墙成槽静置时间的增加,泥浆会发生絮凝沉淀,泥浆液面会不断下降。因此,在成槽施工中,应时刻关注泥浆液面的变化,并及时进行补浆,以保持液面在合理安全的深度。
图 14为槽壁稳定性系数随泥浆重度变化图,由图可知,泥浆重度也是维持槽壁稳定的一个重要因素,槽壁稳定性安全系数随泥浆重度增加大致呈现线性增长。经计算,当泥浆重度为10.5 kN/m3,稳定性安全系数为1.02,当泥浆重度为12.5 kN/m3时,稳定性安全系数增至1.29,增幅达到26.5%。实际上,泥浆护壁作用主要体现在泥浆对槽壁的静水压力,而静水压力与泥浆重度成线性增长关系,因此,为了提高槽壁稳定性,可以通过适当增加泥浆重度来增大槽壁侧向静水压力,但泥浆重度也并不是越大越好,同时还要考虑混凝土的浇筑难易度和沉渣厚度等方面的影响。
图 15为槽壁稳定性安全系数随地面附加荷载变化图,由图可知,稳定性安全系数随地面附加荷载的增加呈现下降趋势。经计算,当地面附加荷载为0 kN/m2时,稳定性安全系数为1.21,当地面附加荷载为40 kN/m2时,稳定性安全系数为0.99,降幅达到18.2%。地面附加荷载每增加10 kN/m2,槽壁稳定性安全系数则下降4.6%。因此,地面附加荷载也会对粉砂层槽壁稳定性产生一定影响,在成槽施工时应尽量使大型机械远离施工槽段,也能使粉砂层槽壁稳定性得到相应地提高。
图 13 稳定性安全系数随泥浆液面深度变化Fig.13 Variation of stability safety factor with slurry level depth
图 14 稳定性安全系数随泥浆重度变化Fig.14 Variation of stability safety factor with mud weight
图 15 稳定性安全系数随地面附加荷载变化Fig.15 Variation of stability safety factor with additional ground load
(1)基于实际工程中粉土夹砂层在承压水作用下的破坏模式对粉砂层槽壁失稳模型进行计算假定,建立三维滑动体计算模型,采用极限平衡原理对粉砂层槽壁失稳进行受力分析,提出承压水作用下粉砂层槽壁稳定性安全系数的计算公式。
(2)通过工程实例进行对比分析,结果表明,本文提出的粉砂层槽壁稳定性理论计算公式基本是可靠的,可为后续承压水作用下粉砂层地连墙成槽施工提供一些理论参考。
(3)基于实际工程案例,采用本文提出的计算公式对槽壁稳定性影响因素进行分析,结果表明,承压水、地下水位、泥浆液面深度以及泥浆重度对粉砂层槽壁稳定性影响较大,尤其是承压水和地下水位是造成粉砂层槽壁失稳最主要因素,地面附加荷载对槽壁稳定性也会产生一些影响,不过和其他因素相比影响较小。
(4)本文提出的承压水作用下粉砂层槽壁稳定性安全系数应根据实际工程安全等级进行安全取值,如何根据实际工程的要求以及考虑不同影响因素进行安全系数的取值有待后续进一步研究。