基金项目:国家自然科学基金项目(42201077,42177453);中国博士后科学基金资助项目(2023M732105);山东省自然科学基金项目(ZR2021QD074);山东省高等学校“青创团队计划”项目(2024KJH087)联合资助。
作者简介:刘耀辉(1991-),男,博士后,副教授,主要从事遥感信息提取、深度学习技术及灾害管理等方面的研究。E-mail:liuyaohui20@sdjzu.edu.cn
通信作者:李晓丽(1982-),女,博士,高级工程师,主要从事灾害信息处理技术、地震灾害评估等方面的研究。E-mail:lixiaoli@seis.ac.cn


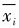 为第i个指标的平均值,σi为第i个指标的标准差。
为第i个指标的平均值,σi为第i个指标的标准差。

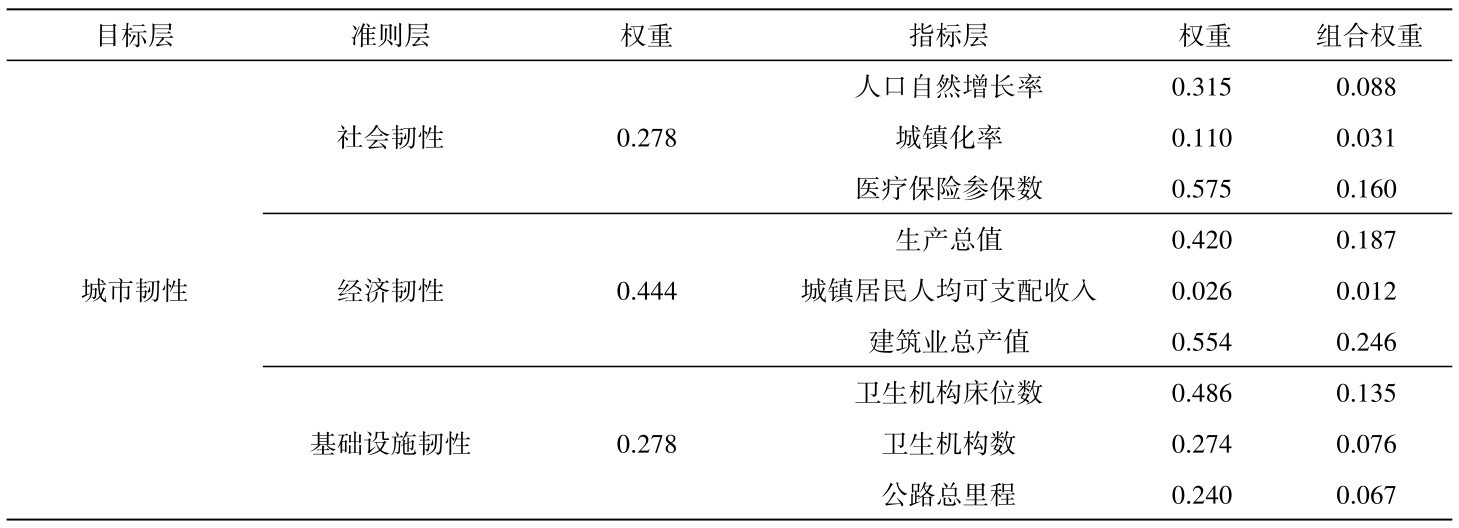
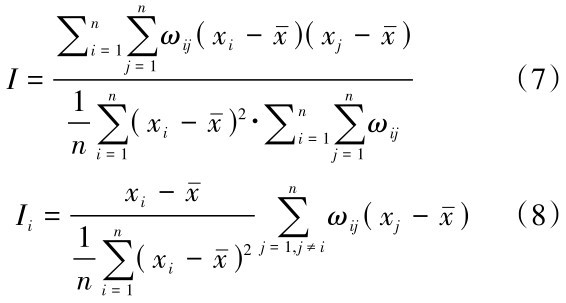
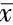 为样本属性均值, ωij为空间对称权重。
为样本属性均值, ωij为空间对称权重。