基金项目:国家自然科学基金(41807265;52308393);江汉大学省部共建精细爆破国家重点实验室、江汉大学爆破工湖北省重点实验室联合开放基金(PBSKL2023B2)联合资助。
作者简介:黄燕(1988-),男,高级工程师,注册土木工程师(岩土),从事岩土勘察设计工作。E-mail:516204562@qq.com
1.重庆市勘测院,重庆 401147;2.重庆大学,重庆 400045;3.中建桥梁有限公司,重庆 402260
1.Chongqing Survey Institute , Chongqing 401147, China;2.Chongqing University , Chongqing 400045, China;3.China State Construction Bridge Co.,Ltd.,Chongqing 402260,China
Micro-vibration;Sliding zone soil;Cumulative damage;Weibull distribution;Constitutive model
DOI: 10.13512/j.hndz.2024.03.11
随着我国经济建设的不断发展以及“一带一路”陆上丝绸之路的不断开拓,爆破作为岩体开挖的主要施工方式,较多的应用于矿山开采与隧道开挖等大型工程中,虽然其推动了经济建设的全面发展,但是反复多次的微振动已逐渐成为了诱发含软弱结构面的缺陷边坡,发生岩体失稳灾害的重要影响因素[1-2],同时在我国建国初期,涌现了大量的开采矿山,随着经济建设的不断进步,这些矿山逐步由露天开采转为地下开采,而地下开采具有开采位置相对集中、开采爆破次数频繁的特点,这使得地下采场内反复多次的爆破开挖对含有滑带土的边坡极易造成破坏[3-4]。故研究高陡边坡滑带土微动力累积损伤机理具有重要的意义。
研究学者从不同角度和层次,通过不同强度屈服准则对岩土体的统计损伤本构模型进行了研究和修正[4-6]。如田振元等结合Lade-Duncan强度准则,研究得到了岩石在三轴试验条件下,能够较好反映岩石应力失效破坏过程的本构损伤模型[7]。但随着围岩所受应力的逐渐增大,岩体的应变软化特性逐渐减弱,岩体的峰值强度与其残余强度的比值逐渐增加,说明初始应力条件影响着岩石应力应变全过程曲线的后半部分[8],而对于受到反复微震影响下的边坡,滑带土的残余强度和峰值强度均是边坡稳定性计算的关键参数,同时岩石的残余强度对其力学参数损伤变量的研究也有着很大的影响[9-10],如曹瑞琅等结合Hoek-Brown屈服准则,建立了能够突出显示岩石在峰值强度后应变软化过程的损伤模型[11],然而针对残余强度对于岩石力学参数的影响,许多学者又将岩石受到的荷载抽象为损伤和未损伤两部分材料共同承担,然后基于Drucker-Prager 准则和Mohr-Coulomb准则,建立了能够反映残余变形的统计损伤模型[12-13]。目前这些关于考虑了残余强度的损伤本构模型主要包括有以下三种:①基于损伤理论和Lemaitre应变等价性假设建立的弹塑性损伤模型[14];②基于损伤恢复变量以轴向应变为损伤演化控制量建立的弹塑性损伤模型[15-16];③基于统计分布建立的岩石损伤本构模型[17-18]。统计损伤模型具有分布连续,能较好的模拟力学性质全过程研究的特点。其中曹文贵等基于Weibull分布函数和微元强度的理念,建立了能够反映结构面与接触面剪切破坏全过程的统计损伤演化模型,但仅考虑了单次不同法向正应力影响下残余强度变形阶段的特征,未考虑累积荷载影响下抗剪强度的变化规律[19]。孙东彦等基于Weibull分布函数构建了考虑冻融循环次数的弹塑性损伤模型,但其未验证微振动荷载对统计参数影响的适用性[20],杨建平等研究表明岩石在受到剪切荷载作用下,其内部粘聚力在峰值强度后逐渐消失,但其仅考虑了不同围压条件下的岩体的残余强度的衰减过程,未对不同微震荷载作用下的岩石抗剪强度的损伤模型进行验证[21]。
本文在传统岩土体统计应力应变本构模型的基础上,假设受反复多次微振动的滑带土土体微元强度服从Weibull分布,引入微振动荷载累积损伤变量,建立了满足Mohr-Coulomb准则的滑带土土体剪切强度衰减累积损伤本构模型。通过与振动台模型试验中反复多次微振动荷载作用下滑带土土体的抗剪强度参数变化的结果进行对比,验证了所提损伤本构模型的合理性和适用性,并结合验证后的损伤模型,对不同微振动参数下滑带土土体损伤变量的变化规律进行了分析。
损伤理论在损伤模型中的研究应用较广,其中大量的损伤模型都是基于Lemaitre应变等效性假设下建立的[22],如下式(1)所示。该假设表明,滑带土土体的抗剪强度主要有两部分组成,一部分为滑带土土体已受到损伤部分,另一部分为滑带土土体未受到损伤部分,且已受到损伤部分不具有任何抗剪强度,如图1所示,其中空白部分是材料的未受到损伤部分,阴影部分是材料已受到损伤部分,其中假定微单元的宏观名义水平剪应力为τ1,未受到损伤部分滑带土土体的有效剪应力为τ'1,已受到损伤部分滑带土土体材料的微观水平剪应力为τr1,损伤百分比为D。
τ1 =τ'1 (1 - D)(1)
由式(1)可知,当滑带土土体完全破坏时,即当D=1时,滑带土土体的名义剪应力必须为0,即剩余抗剪强度为0,这与实际情况明显相反。然而[26],其中假设滑带土土体在发生剪切破坏时,滑带土土体的抗剪强度由岩土体内部已发生损伤部分的剪应力以及未发生损伤部分的剪应力共同组成,如下式(2)所示。
τ1 =τ'1 ( 1 - D )+ τr1D(2)
由式(2)可知,当滑带土土体处于完全破坏状态时,即当D=1时,τ'1(1-D)=0以及τ1=τr1。由公式(2)可1以看出,处于完全破坏状态的滑带土土体仍具有一定的抗剪强度,这与实际情况完全相符,因此,为了建立能够反映岩体微振动剪切强度衰减的累积损伤本构模型,做出了以下假设:
(1)在剪切荷载作用下,滑带土土体中的材料被简化无数个微元组成,主要分为已受到损伤部分和未受到损伤部分,同时岩体所受剪应力由这两部分的抗剪强度共同组成。
(2)在滑带土土体处于剪切破坏的状态下,一些未损伤部分岩土体的应力状态和岩石强度参数满足摩尔库仑破坏准则,如式(3)所示。
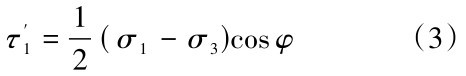
式(3)中:σ1为结构面处于极限破坏状态时的有效第一主应力,σ3为结构面处于极限破坏状态时有效第三主应力。φ为滑带土土体处于极限平衡状态时的内摩擦角。
图1 岩石微单元剪切应力示意图Fig.1 Shear stress for rock microelement
(3)滑带土土体的损伤只发生在水平剪切方向,竖向不发生损伤,即滑带土土体在水平方向的剪应力由材料已受到损伤和未受到损伤两部分材料共同承担,岩石垂直方向的名义法向应力等于有效法向应力。
(4)滑带土土体在受到水平剪应力的作用下,滑带土土体的抗剪强度逐渐增加到峰值强度后迅速下降至残余强度,其中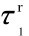 示为滑带土土体的残余应力强度。
示为滑带土土体的残余应力强度。
(5)未受到损伤部分滑带土土体应力—应变关系服从广义虎克定律,即
τ'1 =Gr'1(4)
式(4)中,G为滑带土土体的剪切模量;τ'1为未受到损伤部分滑带土土体剪切应变。
结合式(2)可以看出,当滑带土土体处于完全破坏状态时,可以得到滑带土土体的水平残余抗剪强度τ1=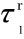 它不随变形的增加而变化。因此式(2)所建立的统计损伤模型更能突出滑带土土体在受到反复多次的剪切破坏作用时,滑带土土体本身剪切强度的累积衰减本构关系,但为了建立该损伤本构模型,首先应该找到其中水平残余抗剪强度
它不随变形的增加而变化。因此式(2)所建立的统计损伤模型更能突出滑带土土体在受到反复多次的剪切破坏作用时,滑带土土体本身剪切强度的累积衰减本构关系,但为了建立该损伤本构模型,首先应该找到其中水平残余抗剪强度 损伤变量百分比D数值的确定方法。
损伤变量百分比D数值的确定方法。
由于滑带土土体材料是由已受到损伤部分和未受到损伤部分的材料共同组成的,它们彼此紧密地混合在一起,根据假设(3)和变形协调原理,可以得到公式( 5 ),其中ri为滑带土土体在发生剪切破坏时整体的剪切应变,r r1为受到损伤部分滑带土土体的剪切应变。
ri =r'1 =r r1(5)
结合摩尔库伦准则得到:
τ1 =σtanφ + C(6)
式(6)中:C为滑带土土体处于极限平衡状态时的内粘聚力。
本文提出的微振动作用下滑带土土体剪切强度衰减的累积损伤本构模型的关键是合理地测量滑带土土体的微观单元强度。为此,通过引入文献[23]和[24]的思想,建立了测量岩石微元素强度F的方法,其表达式如下:
F=τ'1 - τr1(7)
结合式(7)和式(4)得到滑带土土体微元强度F,如式(8)所示。
F=Gnr1 - τr1(8)
式(8)是测量滑带土土体材料微单元强度的方法。其中假设滑带土土体不仅考虑了损伤阈值的影响,其微元强度也服从Weibull分布,则滑带土土体材料的抗剪强度的统计损伤演化模型如式(9)所示。
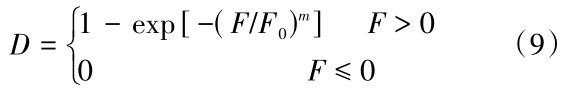
式(9)中m和F0为滑带土土体微单元强度F的Weibull分布参数。因此,结合式(8)和式(9),可以得到剪切试验条件下的统计损伤本构模型,用于模拟滑带土材料剪切强度的累积损伤。
在反复多次微振动累积荷载的作用下,滑带土土体材料的抗剪强度逐渐减小,表现在剪应力以及剪应变曲线上的变化是剪切模量逐渐变小,即可将剪切模量作为滑带土土体材料内部损伤的基本判别标准。定义其损伤变量为

式(1 0)中, G 0 , Gn分别为在受到累积微振动荷载前和n次微振动荷载之后,滑带土土体材料的剪切模量。[8]和[25]中的观点,不同次数微振动荷载和直剪试验的正应力荷载均可以使滑带土的抗剪强度降低,故将两种荷载导致的滑带土的抗剪强度的损伤进行耦合分析,即得到两种荷载总的损伤变量表达式,如式(11)所示。
Dm =D + Dn - DDn(11)
结合式(9)、式(10)和式(11),得到不同次数的微振动荷载和剪切荷载,耦合作用后滑带土土体材料的损伤变量总演化方程,如式(12)所示。
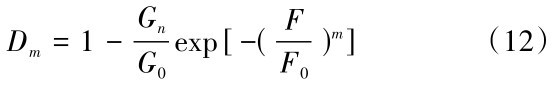
由式(2)、式(4)和式(11)可得到受反复多次微振动的滑带土土体材料微元强度服从Weibull分布,引入微振动荷载累积损伤变量,建立了满足Mohr-Coulomb准则的滑带土土体材料剪切强度衰减累积损伤本构模型,如式(13)所示。
τ'1 =Gnri (1 - Dm)+ τr1 Dm(13)
结合式(3)和式(13),可以得到在主应力状态下,反复多次微振动作用的滑带土土体材料损伤本构方程,如式(14)所示,其可用于模拟滑带土土体材料剪切强度的累积损伤。并且模型参数m和F0的确定是模型建立中的关键问题之一。
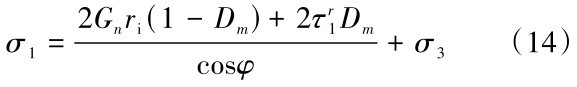
当滑带土土体在经过n次的微振动后,滑带土土体材料在进行剪切试验时,根据岩土材料剪应力—剪应变衰减曲线的极值特征,建立了本构模型参数,如公式(15)所示。同时假设在不同有效法向应力(σ)条件下,滑带土土体材料的峰值剪应力为τmax,峰值剪应力对应的峰值应变为rn 。即当ri=rn时, τ1=τmax。

根据式(6),当滑带土土体材料处于极限平衡状态,也满足以下公式。

[32]中关于分布函数参数的求解办法,即采用全微分的形式,将σ1和σ3均视为关于r1、r3和n的函数,并得到以下公式,其中r1为第一主应力方向的应变,r3为第三主应力方向的应变。
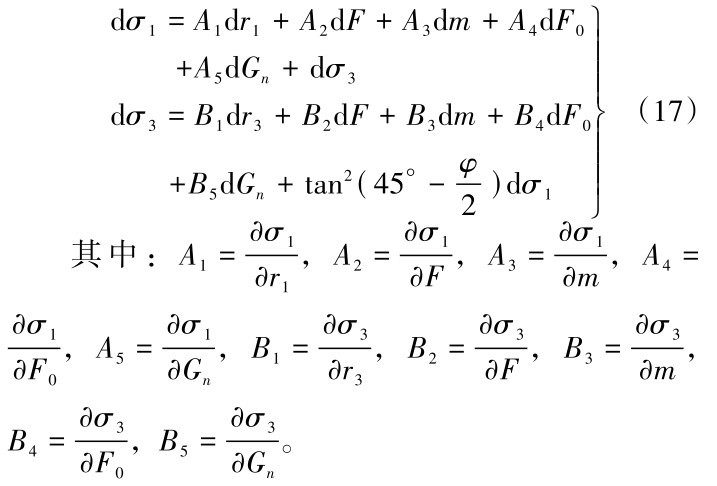
对式(17)中的dF也进行全微分求解,使其成为关于dr1、dr3、dσ1、dσ3的全微分方程。
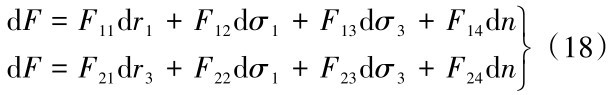
为了消除公式(17)中的dF0、dm、dGn ,将其全部求解为关于dσ3和n的全微分方程。如下式(19)所示。
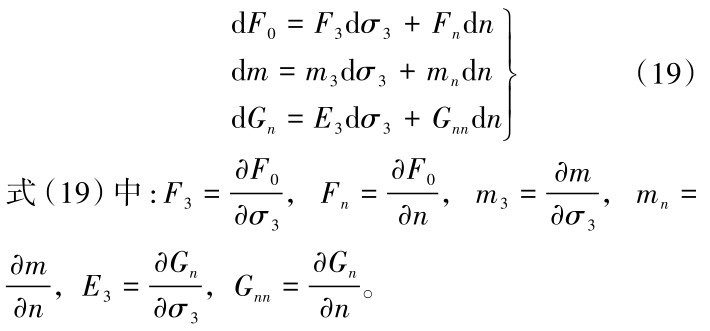
将式(18)和式(19)带到式(17)中得到式(20)。
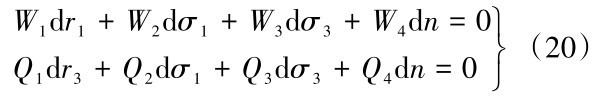
其中: W 1=A1+A2 F11, W 2=A2 F12-1 , W 3=A2 F13+A4 F3+A3 m 3+A 5 E 3+1 , W 4=A 2 F 14+A4 Fn+A 3 mn+A 5 Gnn , Q 1=B 1+B2F21, Q 2=B 2F22, Q 3= B 2F23+B3m 3+B4F3+B5E3-1 , Q4=B2F24+B3mn+B4Fn+B5Gnn。
结合式(16)和式(20)得到式(21)
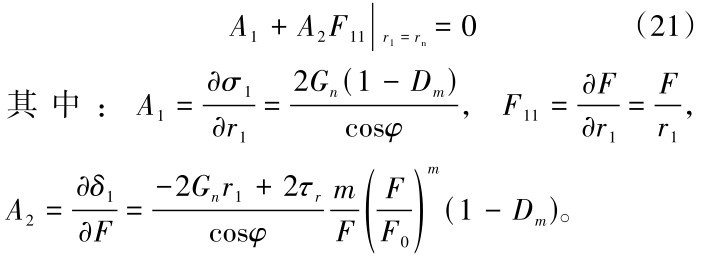
由式(21)求解得到式(22)。
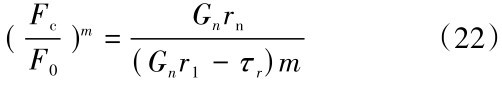
当r 1=rn时, F对应的值为FC ,结合式(1 2)~(1 4),得到(FC/F0)m的表达式,如式(2 3)所示。
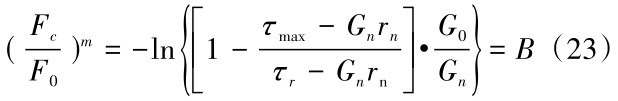
由式(22)、式(23)得到式(24)和式(25)。
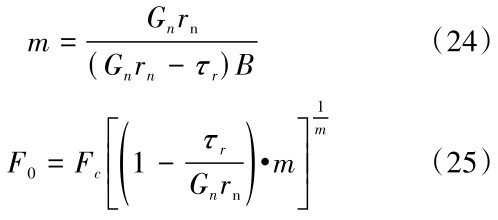
式(23)~(25)即为模型参数与岩石力学特征参量的关系式。参数表达式中所包含的滑带土土体材料的宏观力学量均极易从常规力学特性试验中得到。特别在因试验条件限制难以获得滑带土土体全应力应变曲线的情况下,仍可得出反映滑带土土体材料破坏全过程的本构模型。由式(8)、(12)、(24)、(25)可得到不同次数微振动荷载和剪切荷载后滑带土土体材料的损伤变量总演化方程如式(26)所示。

为了验证理论模型的合理性,结合不同加载强度和加载时间下滑带土土体的峰值粘聚力和摩擦角数据,可以得到滑带土土体材料剪切强度随加载时间和加载强度变化的衰减本构模型,本文引用吴廷尧[26]通过微振动作用下滑带土抗剪强度的劣化规律试验的相关研究成果,来对本文提出的关于考虑微振动荷载累积损伤变量的滑带土统计损伤本构模型的合理性进行验证。表1显示了不同法向应力和加载时间下累积剪切强度损伤理论预测模型的参数值。通过振动台模型试验得到的滑带土剪应力实测值与理论模型预测值进行比较,如图2所示。
由图2可以看出:(1)通过试验数据与理论曲线的比较,可以看出试验结果与理论结果吻合较好。理论模型的预测结果能反映滑带土土体随法向应力和加载时间的衰减趋势。结果表明,考虑水平剪应力残余应力强度的损伤本构模型能充分反映滑带土的衰减变化,同时引入微振动荷载累积损伤变量,建立的满足Mohr-Coulomb准则的滑带土材料剪切强度衰减累积损伤本构模型,能够更好的反映不同微振动参数下,滑带土材料剪切破坏的全应变过程,在相同的微振动加载情况下,滑带土土体的剪应力值随着加载时间的增加而逐渐减小,说明随着加载时间的增加,滑带土土体的抗剪切能力在逐步降低,但随着围岩压力的增加,滑带土的抗剪强度也逐渐增大,说明随着滑带土材料初始应力的增加,滑带土材料的抗剪切破坏的能力在增加,围岩压力越大,滑带土材料越不容易被剪切破坏。
(2)根据岩石屈服的概念,采用极值法确定滑带土土体剪应力预测模型的参数,适用于不同加载参数和围压下的加载试验数据的求解。同时,目前国内外学者大多采用不同强度屈服准则对岩土统计损伤本构模型进行研究,忽略了软岩或结构面反复微振动引起的累积损伤。然而,本文的研究思路具有较大的优势,一方面不含非常规岩石力学参数,对工程应用更为保守。另一方面,在统计模型中考虑了反复多次的微振动的累积效应,较好地反映了累积振动载荷对岩土体统计损伤本构模型的影响。
表1 不同法向应力和加载时间下滑带土土体材料剪切强度累积损伤模型参数值Table 1 Parameter values of cumulative damage model of shear strength for soil in sliding zone under different normal stresses and loading time
基于验证后的滑带土土体剪切强度衰减累积损伤本构模型,结合滑带土土体材料破坏全过程的总损伤演化方程式(26),可得到不同微振动参数作用下滑带土材料损伤力学特性变化规律,如图3所示。
由图3可以看出,反复多次的微振动荷载和直剪试验的正应力荷载耦合作用下,滑带土土体的损伤呈S型变化,其在相同振动强度和围压的情况下,随着微振动加载时间的增加,滑带土材料的初始损伤值在逐渐增加,并且随着微振动加载时间的增加,滑带土土体在正应力加载情况下,其损伤值增加的幅度在减小,且微振动加载时间在180 s和240 s时,两者之间的损伤值变化相差不大,说明随着微振动加载时间的增加,滑带土土体越难发生损伤,且滑带土土体在加载时间较小时,反复多次的微振动荷载和直剪试验的正应力荷载的耦合作用,更容易使得滑带土土体发生破坏。同时滑带土土体围压的增加,使得滑带土土体的初始损伤值在减小,且随着剪切应变的增加,其应变损伤破坏过程在减缓,说明滑带土土体围压的增加,可以提高滑带土材料的抗剪切性能,能够减小材料损伤破坏时的塑性区体积,故而能够提高含滑带土边坡的安全系数。
图2 剪应力实测值与理论模型预测值的比较Fig.2 Comparison of measured shear stress and predicted value by theoretical model
当微振动次数为180 s和240 s时,二者之间的损伤率变化不明显,说明随着微振动次数的增加,滑带土进一步破坏的难度加大,也就是说,微振动次数较小时,滑带土的耦合效应减弱,微振动荷载和正应力荷载的直剪试验更容易引起滑带土的破坏。同时从图3也可以看出,随着断滑带土正应力的增大,滑带土的初始损伤百分数逐渐减小,说明滑带土围压的增大可以提高滑带土的抗剪能力,减小微地震作用下滑带土的塑性区体积,最终提高滑带土的抗剪强度参数。
基于已验证的描述滑带土土体抗剪强度衰减的累积损伤本构模型,结合计算滑带土土体损伤变化率的公式,可以得到不同微振动次数下滑带土土体损伤变化率的演化规律,如图4所示。
由图4可以看出,剪切试验中微振动荷载与正应力荷载的耦合作用并没有改变损伤变化率曲线的形状,在一定的微振动次数下,滑带土土体的损伤变化率先增大,达到峰值,然后随着剪切应变的增大而减小。由图4还可以看出,在滑带土土体变形初期,滑带土土体中少量强度较低的微量元素首先被破坏,而在滑带土土体变形中期,滑带土土体中大量微量元素被破坏,在此阶段,滑带土土体的抗剪强度达到抗剪强度的峰值,在此阶段滑带土土体的宏观破坏特征最为明显。而在滑带土土体变形后期,有少量高抗剪强度的微单元继续承受剪切变形。
图3 不同微振动参数下滑带土土体损伤演化曲线Fig.3 Damage evolution curve of sliding zone soil under different microseismic vibration parameters
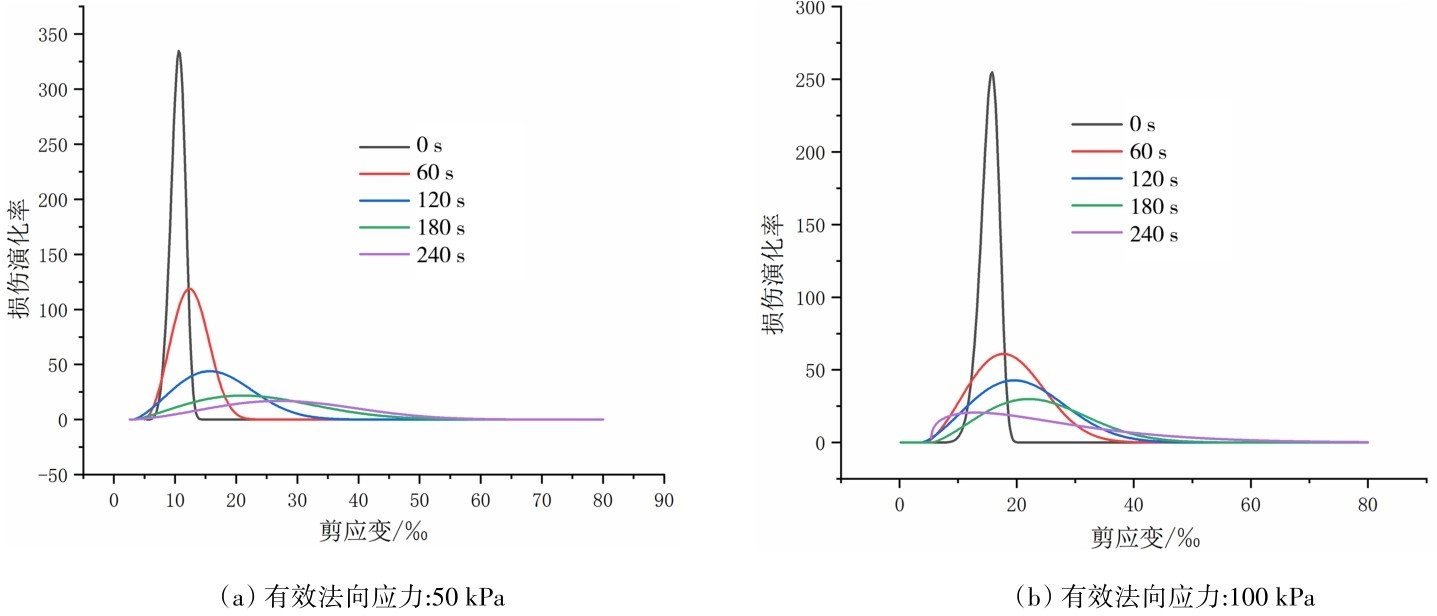
图4 不同围岩应力作用下的滑带土土体的损伤演化率Fig.4 Damage evolution rate of sliding zone soil under different surrounding rock stresses
随着微振动次数的增加或剪切试验法向应力的增加,滑带土土体损伤变化率曲线的峰值逐渐减小,达到上述峰值后,描述滑带土土体损伤变化率曲线的斜率变缓,损伤变化率曲线峰值对应的应变值增大,进一步表明随着微振动次数的增加,滑带土土体内部塑性增强,延性破坏特征越来越明显。
(1)本文建立的考虑微振动荷载累积损伤变量的滑带土统计损伤本构模型,不仅能够更好的反映滑带土材料剪切破坏的全应变过程,也能够反映复杂荷载的耦合作用下,滑带土土体材料累积损伤力学特性。
(2)在反复多次的微振动累积荷载和正应力剪切荷载耦合作用下,滑带土土体的损伤呈S型变化,随着微振动次数的增加或剪切试验法向应力的增加,滑带土土体损伤变化率曲线的峰值逐渐减小,且滑带土土体围压的增加,不但可以提高滑带土土体的抗剪切性能,也能够减小材料损伤破坏时的塑性区体积,故而能够提高含滑带土边坡的安全系数。
(3)本文的损伤预测模型不包含非常规岩石力学参数,对工程应用更为保守,另一方面,统计损伤模型考虑了反复多次的微振动的累积效应,能较好地反映累积振动荷载对滑带土土体剪切强度统计损伤本构模型的影响。因此,本文的研究应更多地应用于反复多次微振动作用下软岩边坡或具有软结构面的高陡矿山边坡的稳定性评价。