作者简介:方英杰(1998-),男,硕士,主要从事物探、防灾减灾等相关研究。
通信作者:宿文姬(1969-),女,博士,副教授,从事地质灾害监测与防护工程研究。E-mail:wjsu@scut.edu.cn
School of Civil Engineering&Transportation,South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510006, China
GPR;Extension cloud model;Urban road collapse;Evaluation index system
DOI: 10.13512/j.hndz.2024.02.09
塌陷是我国地质灾害的常见类型之一,而城市道路塌陷作为塌陷灾害中的一种特定表现形式,虽然规模往往不及山区、采矿区等特殊地区所发生的塌陷,但由于城市地区人口集中,交通繁忙,人类工程活动频繁,其发生的路面塌陷事故频率更高,造成的经济损失更大,社会影响更恶劣,严重影响了城市经济发展与人民安全保障,因此更该引起人们的关注与研究。此外,城市道路塌陷具有隐蔽性与突发性交织,群发性与复发性相结合的特点[1],塌陷过程往往短暂迅速,不对塌陷点所在的整块区域做细致排查的话又很容易使得灾害复发,所以危险性极大。
作为引起道路塌陷的直接致灾因子,脱空、空洞等地下病害潜藏在路面之下,难以察觉。目前,已有多种物探手段应用在城市道路检测上,而探地雷达因其具有精度高、效率高、连续无损、实时成像和结果直观等优点[2],已广泛应用到工程检测和地质勘查中,是近年来地球物理勘探领域研究的热点之一,因此也是针对道路地下病害探测的首选技术手段。
对于地面塌陷的风险评价,国内外做了大量的研究工作,目前常用的评价方法有专家评议法、层次分析法、模糊综合评价、神经网络法、TOPSIS法等定性、定量或半定量评价方法[3-5]。比如,武鑫等人[6]从岩溶发育条件、覆盖层条件和水动力条件这三方面入手,将基于层次分析的模糊综合评价法与GIS技术相结合,对徐州市的岩溶塌陷进行了易发性评价;王子童[7]利用BP神经网络处理煤矿采空区顶板岩性数据的缺失值,构建出基于深度学习中的LSTM模型的采空区地面塌陷危险性评价模型,取得了良好效果;Jiang等研究人员[8]根据环境和人为因素构建出评价指标体系,利用卷积神经网络模型,来评估佛山市的道路塌陷风险,并将风险等级划为五类,绘制出道路塌陷风险图。这些研究不断丰富发展了对于地面塌陷风险的评价思路,但需要指出的是,地面塌陷的成因十分复杂,兼具模糊性和随机性,而以上模型方法未能充分考虑到这点,且在解决定性指标定量化描述、指标等级界限划分存在的模糊随机性等方面存在不足。
本文将由探地雷达检测得到的反映地下病害发育规模的数据,融入进城市道路塌陷易发性评价指标体系中,改进了以往在进行道路塌陷评价时,只考虑环境因素和人为因素这两类指标,与最后的评价目标间的关联性不够强这一问题。此外,可拓云模型能够很好地反映事物评价过程中存在的模糊性和随机性的问题,具有正态云模型的不确定推理特性和可拓学中的物元理论兼具定性、定量的优点[9],但在道路塌陷易发性评价方面上的研究应用较少。因此,本文基于探地雷达检测以及可拓云模型,为城市道路塌陷易发性从指标体系建立到评价方法,提供了一种新的评价思路,并以广州市某市政道路为例,验证最终评价结果更具科学合理性。
典型的探地雷达系统基本可看成由雷达主机、控制单元、接收天线、发射天线这四大部分组成(图1)。当雷达系统利用天线向地下发射宽频带高频电磁波,电磁波信号在介质内部传播时遇到介电差异较大的介质界面,就会发生反射、透射和折射;两种介质的介电常数差异越大,反射的电磁波能量也越大[10]。反射回的电磁波被与发射天线同步移动的接收天线接收后,由雷达主机精确记录下反射回的电磁波的运动特征,再通过信号技术处理,形成全断面的扫描图,工程技术人员通过对雷达图像的判读,判断出地下目标物的实际结构情况。
在可拓学中,通过有序三元组(对象,特征,量值)来形式化描述万千事物及其相互关系,而这样的有序三元组即称为“基元”或者“物元”,用R=(N,c,v)来表示[11]。然而,描述事物特征的量值v是一个明确的评价值域;但在实际情况中,影响城市道路塌陷的因素十分复杂,并且在对风险等级划分以及指标界限取值、数据获取及定量过程均充满了模糊性和随机性。
我国学者李德毅院士率先提出并研究了“云模型”这一方法[12]。云模型以概率论和模糊集理论为基础,将客观事物中的模糊性和随机性进行有机结合,完成定性概念到定量数据之间的自然转换并用统一的数学表达式进行表述[13-14]。在云模型的多种类型中,正态云模型因其普适性而得到了广泛应用,其用三个数字特征( Ex, En, He)进行表示。期望Ex是正态云论域的中心值,是最能够代表定性概念的点;熵En是对定性概念模糊性的度量,熵越大,说明这个概念越宏观,能被度量的范围越广,反映了评价指标的随机性和分级界限的模糊性;超熵He用来度量熵的不确定性,即相当于熵En的熵,它反映了样本出现的随机性,能够将模糊性与随机性进行关联[13,15]。
图1 探地雷达系统组成示意图Fig.1 Composition of GPR system
可拓云模型,即将正态云中的三个数字特征引入并替换掉物元R=( N, c, v )中的量值v[16],使其表示为:
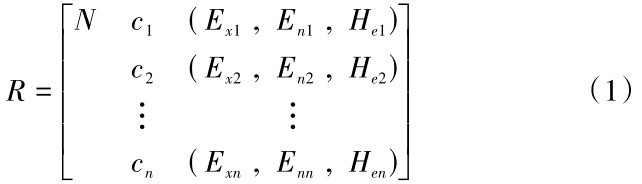
式(1)中,云量值( Exi , Eni , Hei )是对评价指标ci关于等级R下的云描述;N即为被评对象。
在对城市道路塌陷的研究[1,17]中,其成因基本可以归类为“自然因素”:比如气候、水文地质条件等;以及“人为因素”:比如人类工程活动、道路交通荷载等。而在对道路塌陷进行评价时,也往往从这两方面入手进行评价指标体系的建立。以上成因,能够诱发诸如脱空、空洞这类道路地下病害的形成;而地下病害的进一步发育最终导致了道路塌陷。
探地雷达作为现今道路地下病害的常用无损检测手段之一,其能帮助人们识别并获取地下病害的发育规模数据。基于此,本文将这些病害特征数据结合进城市道路塌陷易发性的评价指标体系中,并将评价指标由原本的“自然因素”和“人为因素”扩充完善为“直接诱灾因子”和“间接诱灾因子”这两大类;并且,再参考国家规范JGJ/T 437-2018《城市地下病害体综合探测》、DB11/T 1399-2017《城市道路与管线地下病害探测及评价技术规范》,以及相关文献研究[18-19],建立城市道路塌陷易发性评价指标体系,如图2所示:
图2所示的评价指标体系中,直接诱灾因子为“病害规模”;间接诱灾因子包含了自然因素以及人为因素,将其分为“施工扰动”、“管网影响”、“环境影响”这三类准则;由此建立起两大因素,四类准则,十三项指标的城市道路塌陷易发性评价指标体系。这更为直观清晰地描述了道路塌陷的多重诱因,比以往的指标体系更能直接反映塌陷易发性,使得评价结果的科学准确性大大提升。
对每一指标的具体含义的描述,对之后的量化工作至关重要,其含义说明见表1。需要指出的是,由于不同类型的地下病害对引发道路塌陷的危险程度不同,因此在对前三个指标进行统一评价时,必须再折算上一个相应系数,参照国家规范,脱空、空洞的折减系数取1.0;疏松体取0.5;富水体取0.7。
图2 城市道路塌陷易发性评价指标体系Fig.2 Susceptibility evaluation index system of urban road collapse
表1 评价指标含义说明Table 1 Meaning of evaluation indexes
在综合评价中,对于评价指标的赋权多为采用主观与客观相结合的组合赋权法,然而组合系数的确定通常为主观抉择,使其又丧失了一定的科学性。本文利用客观性的变异系数,对传统的主观赋权法——G1法进行改进[20],既规避了对于组合系数的确定问题,又实现了在指标赋权问题上主观性与客观性的交叉融合[21-22]。其基本思路如下:
(1)根据国家相关规范,以及前人文献研究,再结合专家建议,对评价指标进行重要性程度判别,确定它们的序关系,按重要性程度从大到小排列:
c1>c2>⋯>cj- 1>cj>cj+ 1>⋯>cn(2)
(2)由于各指标的属性与量纲不尽相同,为使其之间具有可比性,需要先对其进行标准化处理:
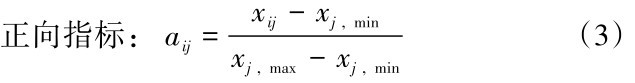
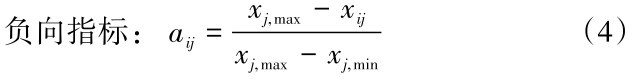
上式中,xij表示第i个被评对象的第j个指标的实测值; xj, max与xj, min分别代表同一个j指标下不同对象间的最大实测值和最小实测值; aij为标准化指标值。
(3)计算指标的变异系数Cj :
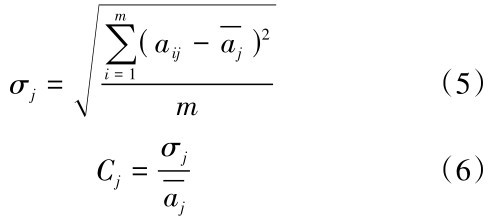
上式中, i=1, 2,⋯m,代表评价对象个数; j=1, 2 ,⋯, n ,代表指标个数; σj为第j个指标的标准差;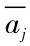 为第j个指标在所有评价对象中的平均值;aij为第i个评价对象的第j个指标下的值。
为第j个指标在所有评价对象中的平均值;aij为第i个评价对象的第j个指标下的值。
(4)利用变异系数之比来确定相邻指标的重要性程度比rj- 1_j:
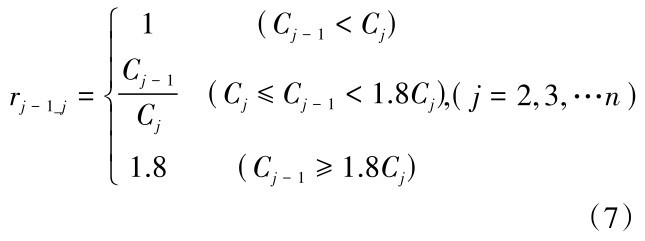
(5)计算指标的最终权重:
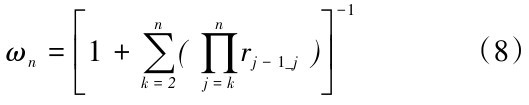
ωn为第n个,即最末位指标的权重,将其乘以对应的重要性程度比rn - 1_n,则可以求出上一位指标权重大小;不断向上反求,则最终可以得到所有指标权重,如式(9)、式(10)所示:
ωj- 1 =rj- 1_j⋅ωj , ( j=n , n - 1 , n - 2 ,⋯, 2 ) (9)
W=[ ω 1 ω 2 ⋯ ωj ⋯ ωn ] (1 0)
本文参考国家相关规范,并结合城市道路塌陷治理中的实际情形,对城市道路塌陷易发性按易发程度从高到低划分出Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ、Ⅳ四个等级(表2)。
确定每一评价指标在四个等级下的等级界限值[ cmin, cmax ],并将其作为一个双约束空间,综合考虑界限划分时的模糊性和随机性等双重不确定性,按公式(10)~(12)计算出每一指标等级界限云模型的数字特征[23]:
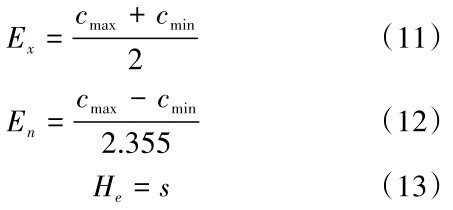
式(13)中,s为常数,可根据评价指标的不确定性和城市道路的实际情况进行调整。在得到云模型数字特征后,根据正态云的生成算法[13],可以得到评价指标云图。
表2 城市道路塌陷易发程度分级表Table 2 Grading for susceptibility of urban road collapse
在城市道路塌陷易发性评价中,本文将其分为四个评级等级,并对每一指标也进行了相应分级;在实际应用中,对于所获得的评价对象的指标实测值,在充分考虑模糊性和随机性的前提下,计算其与每一等级的可拓云模型之间的隶属度μ,可以用下式进行计算:
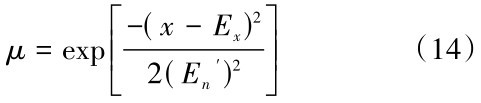
式(1 4)中, x为指标实测值; Ex为其相应指标在每一等级下的期望;En′为服从以En为期望,He为标准差的正态随机数,即En′~( En , He 2 )。
由式(13)可知,由于随机数的存在使得在求取隶属度μ时存在随机性,因此需计算多次取隶属度期望值Ex, μ,如式(19)所示;本文计算2000次。按式(1 5)对Ex , μ进行归一化处理,并最终得到隶属度矩阵U:
Ex, μ_jl ujl =4 ,(l=1,2,3,4;j=1,2,⋯,n)(15)∑Ex, μ_jl l=1 éu11 u12 u13 u14ù êêu21 u22 u23 u24úú U=êê⋮ ⋮ ⋮ ⋮úúêê úú(16) ëun1 un2 un3 un4û
上式中, l=1, 2, 3, 4代表评价等级Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ、Ⅳ级;j为评价指标个数。
由式(10)得到的指标权重向量W与式(16)得到的隶属度矩阵U相乘,得到可拓云综合评价向量K:
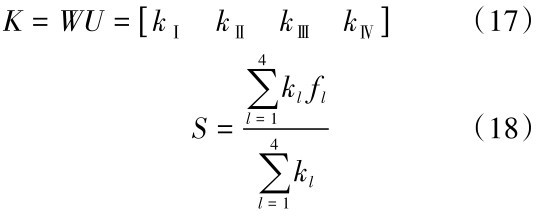
式(1 8)中, S为综合评价分数, fl为等级l的得分,Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ、Ⅳ级分别对应得分4、3、2、1分;最后根据S的数值大小判断属于哪一等级,如表3所示。
引入置信度因子β[24]:
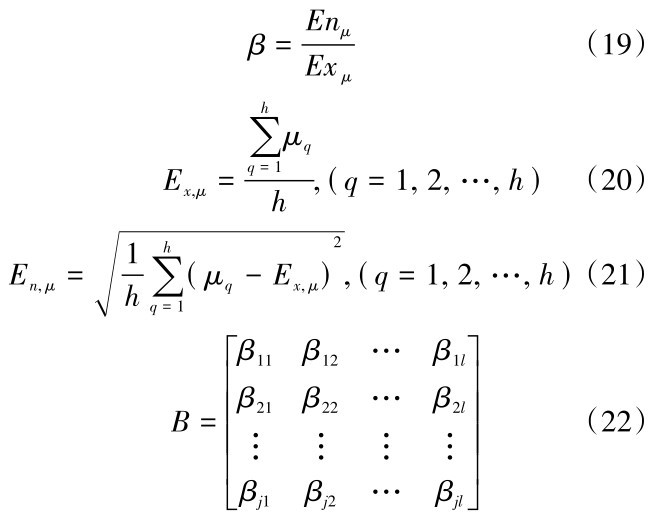
上式中,Ex, μ与En, μ为隶属度μ运算了h次的期望与熵,本文h=2000。按式(19)~(21)计算出每一等级下每一评价指标的置信度因子,形成评价对象的置信度矩阵B ,其中,若小于0.05的β jl占了95%及以上,则可认为评价结果可信。
本次进行雷达检测并评估其塌陷易发程度的广州某市政道路,是连接广州主城区与郊区之间的一级公路。该道路全长18.4 km,设计时速60 km/h,道路整体宽度60 m;其作为一条广州中心城区与郊区快速联系的重要客运走廊,与其他道路一起组成广州对外通道网络。本文依托于该市政道路的地下病害雷达实测项目,对道路全线进行探地雷达检测,获取病害数据,并结合其他评价指标的实测值,对该市政道路塌陷易发性进行评价研究。
在此次工程检测中,以MALA MIRA 8通道三维探地雷达(200 MHz)为主,并辅以Crossover CO730二维探地雷达(70 MHz+300 MHz)进行同步联合检测。在每一行车道上,均按照左车辙和右车辙的位置布置两条三维雷达测线;而由于该三维探地雷达的有效测幅宽度为0.91 m,车道宽度约为3.75 m,因此,二维雷达除了跟随于三维雷达之后进行同步检测外,在实际情况允许下再在两条测线之间进行一次检测,尽可能全覆盖地扫描车道。此外,三维及二维探地雷达在检测过程中的数据采集方式均为车载式,由一辆工程车在前方牵引前进,并在雷达后方一定距离另设置一辆保护车。雷达测线布置方案及现场作业情况如图3、图4所示:
本次项目检测,联合使用了三维和二维探地雷达,除了能使检测范围扩大外,其三维雷达检测图谱与二维雷达检测图谱的相互对比印证,也使得数据的解译准确度大大提高:对各个车道的三维雷达结果进行拼接并插值;通过三维雷达检测结果沿深度进行逐层(每0.1 m)的水平横剖面分析,寻找图像异常等问题;对初步确定的病害进行横剖面、纵剖面的剖切,进一步分析,确定剖切图像是否存在横向轴不连续等异常,确定病害的位置;再解译二维雷达检测结果中对应位置的图像结果,根据已有的物探资料排除明确的地下构筑物后,最终确定病害的类型、尺寸和深度。
在分析了该市政道路全线的雷达数据后,最终共检测出63处地下病害,其中脱空29处,空洞1处,疏松体29处,富水体4处。
道路塌陷的致灾规模往往较小,波及范围基本处于道路面以内。因此,不同于崩塌、滑坡、泥石流等地质灾害的评价以整个行政区域去划分网格,对于道路塌陷的易发性评价,应该根据道路特点,划分出相等里程的路段单元去进行评价工作。该市政道路全长18.4 km,本文以每500 m里程的路段为一单元,对该道路全线共划分出37个评价单元。其中,K7+300~K7+600为一座跨江大桥,不属于本次评价研究对象内。
图3 探地雷达测线布置图Fig.3 GPR survey lines layout
图4 现场检测情况Fig.4 On-site testing situation
按图2所述,建立本文评价对象的道路塌陷易发性评价指标体系,值得说明的是,由于检测期间该道路及其周边未有地铁施工影响,因此仅针对本文所述工程项目,剔除“地铁施工”这一评价指标;并根据2.2小节所述内容,计算出所有指标权重,如表4所示;指标实测值来源于雷达检测数据、该道路地勘资料、钻孔数据等。
按照可拓云模型的评价思路,对各指标进行分级,指标界限值见表5;对于两个定性指标“管材”和“道路现状”,其分级依据来源于规范,在进行评价工作时,根据实际情形判断所属级别,确保总体无误,再咨询项目组专家,与其他路段单元进行横向对比,确定具体数值。根据公式(11)~(13)计算出等级界限云模型的数字特征(如表6所示),在式(13)中,对s的取值根据实际指标的模糊性、随机性,以及对所生成的云模型离散程度的判断,经过不断试验,包括最后的可信度检验而确定。利用可拓云模型生成算法,结合表6数据,编写Python代码,生成各指标的评价云图。本文由于篇幅限制,这里仅展示负向指标“病害体覆跨比”及正向指标“岩溶程度”,见图5。从图上可以看出,指标的每一等级云模型之间界限清晰,且离散程度小,说明分级良好。
表4 评价指标权重Table 4 Weights of evaluation indexes
表5 评价指标等级界限值Table 5 Grade threshold values of evaluation indexes
以单元20(K9+500~K10+000)为例,将其各项指标的实测值,即表6数据都代入可拓云模型中,按式(14),编写Python代码进行2000次运算得到平均隶属度,再依照式(15)~(18),最终计算得到单元20的可拓云综合评价向量以及综合评价分数:
K20 =[ 0.356 31 0.363 78 0.225 02 0.054 90 ] S20=3.021 50
所以该路段单元的评价结果为Ⅱ级。再对其进行可信度检验,得其置信度矩阵:
表6 评价指标云模型数字特征Table 6 Numerical characteristics of cloud model for evaluation indexes
图5 部分指标的评价云图Fig.5 Cloud diagram of partial evaluation indexes
表7 单元20的指标实测值Table 7 Measured index values for unit 20

有超过95%以上的置信度因子β<0.05,因此认为评价结果可信。
对该市政道路的37个评价单元对象依次进行相同的可拓云模型评价法,并用风险四色:红、橙、黄、蓝依次代表评价等级Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ、Ⅳ,最终可视化呈现道路全线塌陷易发等级,如图6所示:
图6 广州市某市政道路塌陷易发性等级图Fig.6 Risk map of collapse susceptibility for a municipal road in Guangzhou City
城市道路塌陷发生在人口稠密区,危害很大;且其成因复杂,兼具模糊性和随机性等双重不确定性。基于此,本文通过使用探地雷达对城市道路进行全线的地下病害诊断,并利用可拓云模型,充分考虑其模糊性和随机性等性质,对城市道路塌陷易发性进行了评价研究。从指标体系的建立,到评价模型的运用,取得了以下结论:
(1)本文通过探地雷达的使用,获取城市道路的地下病害数据,并将其融入到评价指标体系中,一改以往只考虑“自然因素”和“人为因素”这两类成因,将指标体系扩充完善为“直接诱灾因子”和“间接诱灾因子”,更直观科学地反映了道路塌陷的易发程度。
(2)通过变异系数法改进传统的G1赋权法,既规避了主观权重与客观权重在进行组合时对组合系数的选取问题,又保留了对指标赋权时,主观性与客观性的有效结合。
(3)将正态云模型的思想引入到可拓学中,利用可拓云模型评价法,在充分考虑了城市道路塌陷的模糊性和随机性的前提下,实现了定性到定量的有效映射,对城市道路塌陷易发性进行了科学评价;并以广州市某市政道路作为研究实例,表明该模型在工程实践中具有科学有效性。
此外,城市道路塌陷是一个十分复杂的问题,本文研究仅为其提供了一种新思路供以参考。如何更科学全面地描述城市道路塌陷易发性是一个艰深的课题,全面提高评价精度,对评价指标体系与评价方法的研究也应不断地深入研讨。