基金项目:黑龙江科技大学引进高层次人才科研启动基金项目(HKD202133);2022年度黑龙江省省属高等学校基本科研业务费科研项目(2022-KYYWF-0560)联合资助。
作者简介:艾骁(1988-),男,博士研究生,讲师,研究方向为地学空间建模、地震地质灾害预警技术。E-mail:axz.1988@163.com
黑龙江科技大学建筑工程学院,哈尔滨 150022
School of Architecture and Civil Engineering,Heilongjiang University of Science and Technology, Harbin 150022, China
Wenchuan earthquake; Seismic landslide risk; Principal component analysis; Gini index; Artificial neural network
DOI: 10.13512/j.hndz.2024.02.06
地震力长期以来一直被认为是引发山体滑坡的主要因素之一,地震引发的山体滑坡及其次生地质灾害一直被认为是严重的自然灾害之一,会造成大量的人员伤亡和严重的经济损失[1]。为了有效预防和减轻地震滑坡引发的灾害,在地震再次袭击同一地区时,必须了解历史滑坡灾害的产生机理[2]。但是,在一个很大的范围内去确定每个滑坡的产生机理是极为困难的。因此,研究人员通常将区域地震滑坡危险性分析作为最终成果,以将理论分析与实际减灾措施相结合[3]。并且,构建区域滑坡危险性评估模型被认为是目前用于分析某个地区可能遭受滑坡破坏的概率大小的最有效的工具之一[4-7]。目前,地震滑坡危险性评估模型的构建方法借鉴了降雨诱发滑坡危险性评估模型的构建方法,并应用于地震滑坡灾害的预警工作[8-9]。
在区域性地震滑坡危险性评估模型构建的研究中,已经有很多学者提出了不同的评估模型构建方法。目前,用于构建评估模型的方法主要分为两类:一类是以层次分析法(Analytic Hierarchy Process,AHP)为代表的半定量方法[10-11];另一类则是以机器学习法(Machine Learning,MR)为代表的数学评估模型[12-13]。机器学习法的优势在于可以对研究区的多个影响因子直接进行训练,并且不需要先验知识或经验,也不需要统计先验模型即可构建数学评估模型[14-15]。基于上述优点,目前用于构建区域地震滑坡危险性评估模型的方法也主要转向了机器学习法,并且很多学者开始关注不同评估模型构建方法之间的比较与分析[16-19]。但是,由于影响因子自身具有一定的复杂性与多样性,因此如何在众多影响因子中选取最具代表性的影响因子仍需进一步研究。本次研究即以此为出发点,将汶川地震区定为研究区,详细探讨了在不同特征选择方法下,运用人工神经网络构建的评估模型的预测结果之间的差异性。
汶川大地震发生于2008年5月12日,是近百年来中国大陆发生在人口相对密集的中、高山地区的强度最大的一次地震灾害。此次大地震形成了沿龙门山中央断裂与前山断裂的两条较长的地表破裂带,并且引发了至少197 481处滑坡,滑坡总面积约为1160 km2,滑坡分布面积约为110 000 km2 [20-21]。图1为本次选取的研究区范围及汶川地震诱发滑坡分布详图,图中可见本次地震引发的滑坡分布于地表破裂带两侧且滑坡区域总体呈现北东走向。
影响因子的选取是地震滑坡危险性评价的关键步骤,其选取主要与地震滑坡的产生机制、区域特征及学者们的经验有关。地震滑坡影响因子总体可分为地震因子、地形因子、地质因子、环境因子及历史因子这5个类别,本次研究选取了高程、地震烈度、坡度、坡向、坡面曲率、水系距、公路距、断裂距、土地利用、年降水量及归一化植被指数(Normalized Difference Vegetation Index,NDVI)共11个影响因子(表1)。所有影响因子数据均在ArcGIS中进行集成并与研究区的地震滑坡数据一起构成地震滑坡数据库,本次研究将数据格式统一为1 km×1 km的栅格数据。研究区地震滑坡数据类型为点数据,经栅格转换后得到8770个栅格滑坡数据,上述栅格数据构成了本次研究的正样本数据,后经过随机选择等量的非滑坡点构成了负样本数据。
图1 汶川地震诱发滑坡位置分布及研究区位置Fig.1 Distribution of landslides induced by Wenchuan earthquake and location of study area
研究区高程范围为418~5426 m(图2a),高程对滑坡的控制作用主要为两个方面:随高程增加,不合理的人类活动会大大增加滑坡发生的几率;其次,高海拔地区降水较多,可能导致更多的滑坡形成。因此,高程与地震引发的滑坡分布之间存在十分复杂的关系,甚至有一些研究人员认为高程对滑坡的产生几乎没有贡献[22-24]。
研究区坡度范围为<65o(图2b),坡度的大小直接描绘了斜面的倾斜程度,均匀、陡峭的斜坡使得物体沿坡面滑动时有着更大的重力分量,故坡度较大的地方更容易产生滑坡[25]。
坡向反映了坡面的朝向,不同朝向的坡面受到光照、温度及降雨量的影响可能不同,这将对植被的类型和分布产生影响。并且,它也会影响坡面的风化程度,导致在风化程度较高的地区更容易发生滑坡[26]。
研究区的斜坡曲率范围如图2d所示,斜坡曲率也是对地震滑坡产生影响的一个因素。斜坡曲率的数值反映了斜坡的平面形态,其中,曲率为负值代表斜坡为凹坡,曲率为正值代表斜坡为凸坡,曲率值为0或接近0则代表斜坡的坡面较为平坦。通常凹面和凸面的斜坡与平坡相比更易产生滑坡。
地震烈度简称烈度,指某一地区的地面和各人工建筑物遭受一次地震影响的强弱程度[27]。在高烈度区,地震滑坡往往密集成群,滑坡出现的频次随着烈度的增高而增加[28]。从图2e中可见,研究区最高烈度达Ⅺ级,研究区内随着烈度的降低,滑坡的密集程度也逐渐减小。
靠近水系的区域坡面岩土体的含水率较高,甚至会被水饱和。同样,距离水系越近,坡脚的侵蚀程度也越高。因此,水系距也被认为是对地震滑坡产生影响的一个重要因素。本次研究以250 m的距离作为间隔建立缓冲区,缓冲区最大距离为1500 m,其余均分为大于1500 m区域(图2f)。
道路的建设通常会对边坡产生一定程度的破坏,同时也会引起渗水导致斜坡的进一步崩塌[29]。因此,公路距被认为是反映人类活动对斜坡产生影响的重要因素之一。与水系距相同,本次研究以250 m作为间隔建立缓冲区,缓冲区最大距离为1500 m,其余均分为大于1500 m区域(图2 g)。
由地震引发的山体滑坡通常沿发震断层呈线性分布(图2h)。越靠近断层的区域,构成斜坡的物质的非连续性越明显。斜坡中的不连续面越多,则越容易产生滑坡[30-33]。一般情况下,随着断裂距的增加,滑坡的数量和规模都会明显降低。
人类对自然环境不合理的利用例如填挖方、采矿、过度开垦等都会对当地的斜坡产生破坏进而引发山体滑坡,其中,土地利用图(图2i)可以最为直观地展现人类活动,是进行地震滑坡危险性分析的一个重要的影响因素。
研究区年降水量范围为503~1634 mm(图2j),降水量与滑坡的联系主要体现在三个方面:①短时间内的强降雨会对坡体产生强烈的冲蚀作用,灌入裂缝产生静水压力;②降水会使得滑坡体的自重增加,下滑力增加;③雨水会增加滑带土孔隙水压力,使得土体抗剪强度大幅下降,抗滑力减小[34]。
表1 汶川地震区数据类型与来源详表Table 1 Detailed table of data types and sources in the Wenchuan earthquake area
归 一 化 植 被 指 数(Normalized Difference Vegetation Index,NDVI),反映了地表被植被覆盖的程度。其计算公式如下:
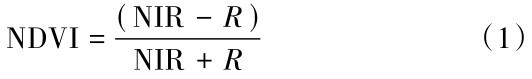
式(1)中:NIR为近红外光波段;R为红光波段。
研究区归一化植被指数范围为0~0.8(图2k),表示大部分地区均有植被覆盖,且数值随覆盖度增大而增大。植被覆盖在山体上,能够减缓雨水对坡面的冲蚀作用,同时植被强大的根部可以加固坡体土质。但是,若一些植物物种的根系不发达,会加大滑坡发生的概率,并且,新种植的植被由于根部扎根不深,不仅不能起到保护坡体的作用,反而会增加斜坡的荷载,引发滑坡。
图2 汶川地震滑坡影响因子平面图(据艾骁[35],2021,有修改) Fig.2 Plan figures of influencing factors of landslide in Wenchuan earthquake area(modified from Ai [35],2021)
本次研究采用相关性系数、主成分分析及Gini指数三种特征选择方法,并基于上述三种方法进行影响因子的筛选,将筛选后的影响因子作为评估模型的输入特征。
相关性系数可以分析影响因子间的相关性,计算公式为:
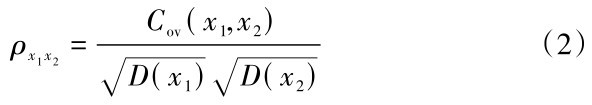
式(2)中,ρ表示两变量的相关系数,Cov表示协方差,D表示方差。相关系数用于表示两个变量之间的线性关系:当ρ x 1 x 2=0,表示变量x1与x2不相关;当ρ x 1 x 2>0,表示变量x1与x2正线性相关;当ρ x 1 x 2<0,表示变量x1与x2负线性相关。其中,数值越大,表示量变量相关性越强。
运用Python构建影响因子间相关性系数后可绘制相关性详图(图3),图中可见地震烈度与断裂距二者之间呈现出极强的负相关性(-0.87),且地震滑坡与坡向之间的相关性最小(0.0031)。经过对于相关性系数的分析,在下一步进行评估模型构建之前可将地震烈度与坡向两个影响因子剔除。
图3 汶川地震区影响因子线性相关性详图Fig.3 Linear correlation of influencing factors in Wenchuan earthquake area
主成分分析(Principal Component Analysis, PCA)是一种常用的多维数据集降维方法,其原理是通过线性变换将原始数据映射到一个新的坐标系中,使得在新的坐标系下数据集的方差最大化。这样可以找到数据中最重要的特征,并实现数据的降维。通过主成分分析计算累积贡献率的过程包括下述几个步骤:
(1)数据预处理:对原始数据进行去均值处理,使得数据的均值为零;
(2)协方差矩阵计算:计算协方差矩阵或者相关矩阵来衡量数据之间的关联性。协方差矩阵的每个元素表示两个变量之间的协方差;
(3)特征值分解:对协方差矩阵进行特征值分解,得到特征值和对应的特征向量。特征值代表了每个特征对总体方差的贡献程度,而特征向量则表示了在新坐标系下各个特征的权重;
(4)特征选择:根据特征值的大小,选择前k个最大的特征值对应的特征向量作为主成分。这些主成分是数据中最主要的特征,它们能够解释数据中大部分的方差;
(5)计算累积贡献率:对选取的主成分,计算每个主成分的方差贡献率。方差贡献率等于该主成分的方差除以所有主成分的总方差之和。然后将方差贡献率按照大小排序,并计算累积贡献率,即前n个主成分的方差贡献率之和。
通过计算特征的累积贡献率,我们可以确定在保留足够信息的情况下选择多少个主成分(表2,图4)。通常,我们希望保留累积贡献率较高的主成分,例如累积贡献率达到90%以上。这样可以减小数据维度,同时保留大部分的信息。
表2 汶川地震区影响因子累积贡献率详表Table 2 Cumulative contribution rate of influencing factors in Wenchuan earthquake area
图4 汶川地震区影响因子累积贡献率综合柱状图Fig.4 Comprehensive histogram of cumulative contribution rate of influencing factors in Wenchuan earthquake area
该方法主要通过随机森林模型计算每个特征的重要性,于随机森林中获取特征重要性的方法主要有三种:Gini指数(Gini Importance),此方法用于计算每个特征在决策树的节点上进行划分时Gini系数的改善情况;基于平均准确率减少(Mean Decrease Accuracy),此方法将特征的值打乱后检测模型的准确率下降的程度,准确率下降越多,特征的重要性越大;基于平均不纯度减少(Mean Decrease Impurity),此方法计算每个特征在决策树中用于划分节点时不纯度的减少程度。本次研究主要采用Gini指数判断特征重要性。
Gini指数是衡量决策树节点不纯度的一种常用指标,用于评估特征在随机森林中的重要性。Gini指数的计算原理如下:
(1)对于一个给定的节点,假设有K个类别,每个类别的概率为p(i),其中i=1,2,...,K;
(2)Gini指数可以通过以下公式计算:
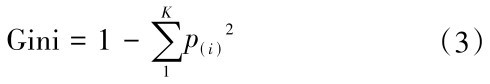
式中,Σ表示对所有类别进行求和;
(3)如果某个节点的Gini指数越小,表示该节点的不纯度越低,即样本的类别分布越集中。
Gini指数在随机森林模型中的具体应用如下:
(1)随机森林中的每个决策树,在构建的过程中,模型会自动计算每个特征在每个节点上的Gini指数改善情况;
(2)对于上述Gini指数改善情况,通过计算每个特征在整个随机森林中的平均Gini指数改善情况(Mean Decrease Gini)作为该特征的重要性得分。
通过计算每个特征的Gini指数改善情况,可以评估每个特征在评估模型构建中的贡献度大小(表3,图5)。即当某个特征在节点上的Gini指数改善越大,表示该特征在划分节点时能够更好地提高样本的纯度,因此该特征被认为是更重要的特征。
表3 汶川地震区影响因子累积重要程度详表Table 3 Cumulative importance of influencing factors in Wenchuan earthquake area
图5 汶川地震区影响因子累积重要程度综合柱状图Fig.5 Comprehensive histogram of cumulative importance of influencing factors in Wenchuan earthquake area
人工神经网络的首个模型及练算法被提出后,即被广泛地应用于模式识别与分类问题[36-37]。众多人工神经网络算法中以误差反传算法即BP(Back-Propagation)算法最为典型,本次研究即是采用误差反传算法进行数学建模。人工神经网络模型的建模流程可总结为如下五个步骤:确定网络结构、选择训练或学习算法、确定激活函数、调节权重及其它超参数、输出结果。
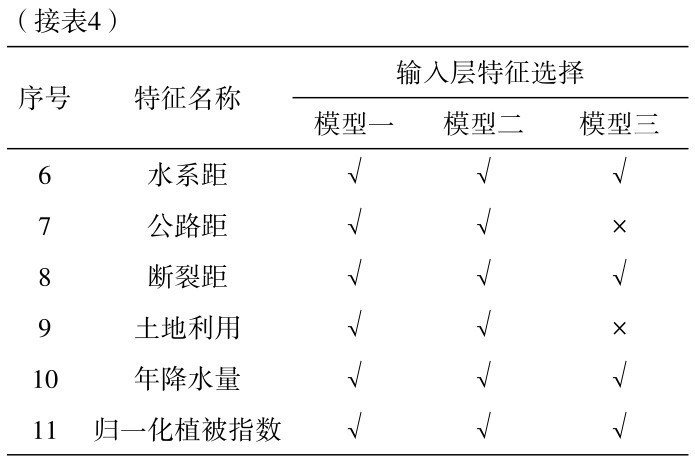
人工神经网络的整体结构可分为输入层、隐藏层和输出层三个部分。在使用人工神经网络进行数学建模之前,确定其基本结构是首先要解决的问题。根据上节对于特征的选择,基于相关性系数、主成分分析和Gini指数法确立三种模型输入层特征,并将上述三种模型定义为模型一、模型二和模型三。其中,输入层所选取的特征详见表4。
表4 人工神经网络输入层特征选择详表Table 4 Feature selection of input layer of artificial neural network
隐藏层方面,本次研究选取单隐藏层结构,因为在以前的研究中发现,当使用两个以上的隐藏层进行预测时,往往会导致对于预测结果的高估,并且,模型的训练时间也会大大增加[38]。隐藏层神经元的数量通常根据以下经验公式确定:
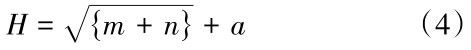
式(4)中:H为隐藏层神经元数量;m为输入层神经元数量;n为输出层神经元数量;a为1~10之间的调节常数。本文将隐藏层神经元个数定为6个。
在输出层的选择方面,选用双输出模式,通过正负样本的训练,最终直接输出相关概率值并将其作为衡量某点发生滑坡与否的标准。
综上所述,本次研究选用的三种人工神经网络模型结构如图6~8所示。
图6 模型一人工神经网络结构示意图Fig.6 Artificial neural network structure of Model 1
图7 模型二人工神经网络结构示意图Fig.7 Artificial neural network structure of Model 2
图8 模型三人工神经网络结构示意图Fig.8 Artificial neural network structure of Model 3
确定了本次研究的三种网络结构后,即可运用神经网络进行分类任务,其总体可概括为两个阶段:训练阶段和分类阶段。
分类阶段所进行的则是将训练好的神经网络模型通过前馈传播的方式对整个数据集进行分类,最终形成相应的预测结果。
模型训练阶段的主要任务是通过误差反传算法来调节模型内部的权重值,直至神经网络的期望输出值和实际输出值之间的误差达到某个预先设置好的最小误差。以模型一为例,本阶段8770个地震滑坡点组成的正样本及随机选取等量的负样本所形成的数据集被分为两个子集:训练集和测试集。其中,训练集运用误差反传来调节模型内部权重,测试集则用于测试每次调节内部权重后的评估模型的具体精度。
在数据集的划分方面,主要有两种方法:一种是将数据集的80%作为训练集,剩余的20%作为测试集;也有一种是将数据集的70%作为训练集,剩余30%作为测试集。本次研究选取第一种划分方法对三个神经网络进行训练。
神经网络训练完成后,将全部数据输入模型,模型通过前馈传播的方式输出结果。样本的模拟数值越接近0,说明此斜坡单元越稳定,发生地震滑坡的可能性越小;反之,样本的模拟数值越接近1,说明此斜坡单元越不稳定,发生地震滑坡的可能性越大。
运用上述三个模型的评估结果,结合ArcGIS软件的空间分析功能,形成三组地震滑坡危险性分级。采用相等间隔分类方法将概率值划分为5个类别,分别对应非常低、低、中、高和非常高这5个地震滑坡危险性等级(图9)。图中可见,由三组模型所生成的图件都可以对研究区进行地震滑坡危险性等级的划分。但由模型一与模型三生成的区划图中,危险性等级为非常高的区域过大,宏观上对于非常高危险性等级区域的划分精度要选低于模型二。
图9 汶川地震区地震滑坡危险性分级Fig.9 Risk classification of seismic landslides in Wenchuan earthquake area
频率比(Frequency ratio, FR)通常用于反映某个因素同属性区间对地震滑坡危险性的影响程度[39]。其计算公式如下:

式(5)中:e代表每个属性区间中滑坡个数;e’代表滑坡总数;E代表该属性区间单元格总数;E’代表研究区总单元格数。得到的频率比值越大于1代表该属性区间对滑坡的影响越大,越小于1则代表该属性区间对滑坡的影响越小。得到频率比以后,计算地震滑坡危险性等级为高与非常高的频率比之和与全部频率比之和的比值,即频率比精度(表5),频率比精度的定义为滑坡易发性等级的非常高与高的两个区间内频率比值的和与所有区间频率比值和的比例[40]。通过表5可见,模型二危险性等级为高与非常高的两个区域的频率比(0.53、3.98)明显高于另外两个模型。且模型二的总体频率比精度(0.92)要高于模型一(0.91)与模型三(0.91)。
通过表5可见,模型二危险性等级为高与非常高的两个区域的频率比(0.53、3.98)明显高于另外两个模型。且模型二的总体频率比精度(0.92)要高于模型一(0.91)与模型三(0.91)。
ROC 曲线全称为受试者工作特性曲线(Receiver operating characteristic curve)。首先,基于预测结果,将结果进行从1到0的反序排列。然后采用不同的阈值,即可得到ROC曲线的横坐标“假正确率(False Positive Rate, FPR)”与纵坐标“真正确率(True Positive Rate,TPR)”。曲线绘制完成后,其下方面积(Area under ROC curve, AUC)即被用来评价模型的精度(图 10),AUC越接近1,模型的精度越高。当AUC为0.9以上时,说明评估模型预测的准确性极好,并且曲线越接近坐标轴的左上方,预测效果越好[41-42]。图中可见,三组评估模型的AUC均达到了0.9以上,模型二的准确率最高,达到了0.933。并且,模型二的曲线形态明显优于另外两个模型,整体居于坐标轴的左上方。
表5 地震滑坡危险性等级频率比精度详表Table 5 Frequency ratio accuracy for seismic landslide risk level
图 10 模型ROC曲线对比详图Fig.10 Comparison of ROC curves of models
本次研究主要围绕以下两个核心议题进行探讨:
(1)影响因子的数量对评估模型的作用。在评估模型的构建过程中,选择适当数量的影响因子至关重要。选择过多的影响因子可能导致模型过度复杂并增加过拟合的可能性;而选择过少则可能导致遗漏关键的信息,进而影响到模型的准确性和稳定性。为了达到模型的最优表现,不仅要平衡影响因子的数量,还需确保所选择的因子是相关并有意义的。在“模型一”的数据预处理中,发现地震烈度与断裂距两个影响因子之间呈现出明显的负相关性。为了避免模型冗余,选择移除地震烈度这一影响因子。为了进一步验证这一观点,笔者重新将地震烈度纳入“模型一”并构建了一个对比模型,命名为“模型四”。从ROC对比曲线图(图 11)可以看出,模型一与模型四在预测精度上的表现几乎没有差异(0.925、0.928),这说明模型一能够在不损失模型预测精度的前提下降低数据维度,避免模型冗余。
(2)主成分分析法的利弊。经过本次研究成果可见,通过三种建模方法输出的评估模型预测结果有所差异。无论是从生成的危险性分级,还是频率比精度与ROC曲线的精度对比,基于主成分分析法构建的数据集的模拟结果均为最优。
但是,主成分分析法并非没有缺陷。该方法主要针对数据集内的特征进行分析,而可能忽略了特征值与标签值间的关系。此外,随数据集维度的变化,预测结果亦可能受到影响。
因此,本研究仅能确认,在当前的数据集条件下,采用主成分分析法筛选特征后的模型具有较高的预测精度。但对于一个更具普适性的特征选择方法,仍需进行深入研究。
图 11 模型一、模型四ROC曲线对比详图Fig.11 Comparison of ROC curves between Model 1 and Model 2
本次研究以汶川地震区的地震滑坡点及与其空间对应的11个影响因子组成的数据集作为研究对象,详细地讨论了在人工神经网络评估模型中采用不同的特征选取方法后构建的评估模型所产生的预测结果的差异性并取得了如下结论:
(1)运用相关性系数、主成分分析及Gini指数三种不同的特征选取方法对数据集中每个特征的重要程度进行分析,得到了完全不同的结果;
(2)由三组模型所生成的地震滑坡危险性分级中,运用主成分分析法构成的数据集构建的评估模型,对于非常高危险性等级区域的划分精度最高;
(3)运用主成分分析法构成的数据集构建的评估模型,相比另外两个评估模型,频率比精度达到了92%(0.92), ROC曲线的预测精度达到了93.3%(0.933),均为三组评估模型中的最高值。
本次研究旨在为相关研究人员在地震滑坡危险性评估模型的构建方面提供一定的思路,并为后续综合多个地震区、多组特征组成的不同维度的数据集构建一个具有普适性的特征选择方法提供一定的理论基础。