基金项目:广东省自然资源厅科研项目(GDZRYKJ2020002、GDGTKJ2018004)
作者简介:姚小月(1996-),女,在读研究生,主要从事边坡地质灾害防灾减灾研究。E-mail:yxy1142194318@163.com
通信作者:宿文姬(1969-),女,博士,副教授,主要从事地质灾害防灾减灾研究。E-mail:wjsu@scut.edu.cn
1.1.华南理工大学土木与交通学院,广州 510640;2.2.广东省地质环境监测总站,广州 510510,;3.3.广东省地质工程公司,广州 510000
1.Department of Civil Engineering , South China University of Technology , Guangzhou 510640, China;2.Guangdong Geological Environment Monitoring Station , Guangzhou 510510, China;3.Geological engineering Company of Guangdong Province , Guangzhou 510500, China
Geological disaster; Risk assessment; Logistic regression; Multi-scale geographically weighted regression
DOI: 10.13512/j.hndz.2023.03.12
地质灾害是在孕灾自然环境和外部诱发因素的综合作用下发生,对承灾体产生不同程度影响和破坏,威胁人民生命财产安全和国家经济发展。具有危害性、可变性、不确定性以及复杂性等特征[1]。广东省是我国十二个地质灾害多发省份之一。省内低山丘陵多,中低山丘陵区和盆地边缘断裂构造发育、风化壳和残坡积层发育、软弱土层广布,且近万年大规模海侵后堆积滨海相溺谷湾淤泥。其次,省内水系众多,水力侵蚀地面,一些地方隐伏碳酸盐岩岩溶发育。再者,广东省人口众多,城镇化进程快,山区削坡建房很普遍。以上这些都导致广东省即便是小规模灾害,都潜在极大危害的特殊性。“十三五”期间,全省共发生地质灾害1155起,造成65人死亡,18人受伤,直接经济损失1.79亿元。灾情最重年份的2013年、2016年和2018年,地质灾害数量分别列全国第3、第8和第6位,死亡人数分别列全国第6、第7和第4位。且近年来,地质灾害多发生在不在册隐患点上,造成人员伤亡和经济损失,从某种程度上讲,完全杜绝地质灾害发生是不可能的,因此,做好地质灾害危险性评价并提前防控,是当前防灾减灾的重要工作。
国内的地质灾害风险评价经过了几十年的发展过程,专家学者对评价体系进行了大量的研究,从不同角度提出了理论框架和技术流程[2-5]。目前较主流的观点是借鉴Westen、Fell等[6-7]提出的理论发展而来,认为地质灾害风险评价包括易发性评价、危险性评价、易损性评价及风险评价几个部分。吴树仁等[8]根据诱发地质灾害的因素不同对易发性和危险性进行区分,定义内部物质条件作用下地质灾害发生可能性为易发性,在易发性评价的基础上引入外部诱发因素的地质灾害发生可能性为危险性评价。我国地质灾害危险性研究。对象从滑坡到多灾种,从单个边坡到区域;内容从对单体灾害的基本特征如地形地貌条件、大小规模等到更深层次的成灾机理、物理力学特征等,再到区域性的危险性综合评价;评价方法从定性、半定量到定量逐渐趋于系统;在调查手段上,从传统的人力野外调查记录到集高分辨率卫星遥感影像、无人机航测、原位监测设备等的空天地一体化技术方法,以及基于互联网大数据的综合信息平台。地质灾害危险性评价研究和实践都取得了突破性的成果。
对于较大区域的危险性评价,确定性方法无法实现,通常是采用概率统计方法,主要如信息量法、证据权法、模糊综合评价法、线性回归、人工神经网络、逻辑回归等。各评价模型均具有各自的优点和不足。
综上所述,本文选取广东省平远县作为研究区,分析地质灾害发生的特征,选取一定的评价因子,综合各模型的特点,采用多个组合模型,分别构建地质灾害危险性评价体系,并通过精度分析与讨论,以求探索出更适合广东省低山丘陵区的地质灾害危险性评价方法。
对于连续型评价因子数据,合理的状态分级直接关系到后续统计分析结果的可靠性,从而影响最终的评价结果。
传统的等距分类本质上是假设样本点在某一评价因子取值范围内均匀分布,从而将其分为间距相等的类别。这一假设太过理想,针对地质灾害的分布很难满足。也就是说,对于指定的评价因子,实际发生的地质灾害在评价因子值域中的分布并不均匀。因此,等距分类可能会引入误差,并经过层层传递和累积放大,最终影响到评价结果。
快速聚类法区别于等距分类法,通过反复迭代更新每个类别的聚类中心,以达到将样本按照同一类别分布尽可能相似,而不同类别内分布尽可能不相似的结果,属于无监督学习。分类结果更符合实际,原始数据的特征也保留得更好。其核心思想是,将n个样本分为k个类别,并计算每个数据p到对应聚类中心mi的距离平方和E,重复多次使E尽可能小,如式(1)。

式(1)中, mi是Ci的均值。
信息量模型最早由Shannon提出,殷坤龙等[2]首次将其应用到地质灾害风险评价领域。

式(2)中, ni , j为第i个评价因子第j区间的灾点个数;si,j为第i个评价因子第j区间的分布总面积;n表示研究区内总灾点数;s表示研究区总面积。
证据权模型是一种以贝叶斯统计为基础,综合各因子以预测某时间发生概率的定量评价方法[9]。
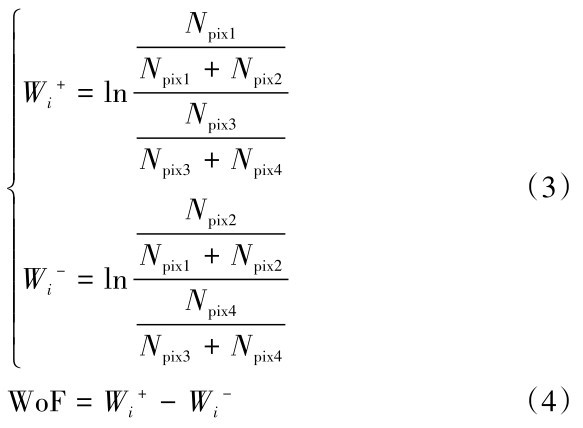
式(3)、(4)中,Npix1表示该评价因子级别内存在灾点的栅格数;Npix2表示该评价因子级别外存在灾点的栅格数;Npix3表示该评价因子级别内不存在灾点的栅格数;Npix4表示该评价因子级别外不存在灾点的栅格数。W+i 表示该评价因子级别内发生地质灾害的正相关系数,W−i 表示该评价因子级别内部发生地质灾害的负相关系数。两权重之差是权重对比度WoF,代表该评价因子级别内地质灾害发生的权重。
对于地质灾害危险性评价,多变量统计分析是对一定大小的样本单元,提取所有评价因子的值,确定每个单元有无地质灾害点分布,从而生成相关矩阵,然后用多次回归或判别分析对矩阵进行分析。
Logistic回归模型是研究二分类因变量与多个自变量之间复杂关系的一种常用多元统计分析方法,是一种广义的线性回归分析模型。以其计算便捷,明确等特点广泛应用于地质灾害危险性评价。在进行评价时,以地质灾害是否发生为因变量(1代表发生,0代表不发生),各评价因子指标值作为自变量。用Pi表示灾害发生概率,则1 − Pi为灾害不发生概率。对Pi/(1 − Pi )取自然对数为ln [ Pi/( 1 − Pi ) ],记为LogitP,取值范围(-∞,+∞),据此建立逻辑回归方程:
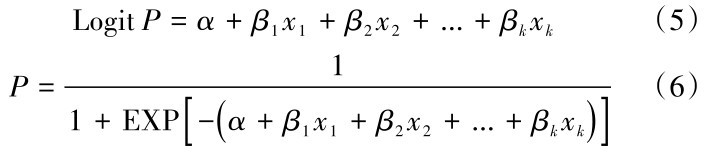
式(5)、(6)中, β 1~βk为权重系数。
地理加权回归模型(geographically weighted re⁃gression model,GWR),本质也是线性回归,是对一般线性回归的扩展。一般的线性回归得到的回归参数实际上是整个区域的均值,属于全局性质的回归。忽略了变量间关系在不同空间位置的差异。而在实际研究过程中,不同地理空间位置由于孕灾条件等方面的现实差异,回归参数往往表现不同。为了解决这个问题,Fortheringham等[10]基于非参数建模的思想,引入局部光滑思想,提出了地理加权回归模型。将空间位置嵌入到回归系数计算之中,从而得到不同空间位置因变量与自变量之间不同的关系函数。因此相对一般的线性回归,地理加权回归是一种能有效解决不同空间位置变量关系的差异问题,处理空间非平稳性的建模技术。
多尺度地理加权回归模型(Multi-scale Geo⁃graphically Weighted Regression,MGWR)作为GWR模型的最新拓展形式,是一种基于有效带宽优化从而使每个自变量都具有不同的空间带宽的地理加权回归方法。其在GWR模型的基础上增加了空间平稳项,引入全局和局域变量,揭示空间非平稳性和平稳性分布[11]:

式(7)中: yi为因变量; i=1 ,…, n ; j为自变量个数;( ui , vi )为第i个样本点的空间坐标;αj为全局变量的回归系数;βj为局部变量的回归系数;εi为第i个区域的随机误差;xij为第j个变量在第i个点的观测值。
不同评价模型均具有各自的优点和不足。双变量统计分析往往是针对两个变量之间的相关关系。信息量模型和证据权模型是两种常见的双变量统计分析模型。其中,信息量模型是通过计算条件概率得到评价因子的权重值。证据权模型的基础是各评价因子之间需满足独立性检验,且要求样本数据足够多。多变量统计分析一般指多个自变量与一个因变量相关关系。逻辑回归模型和多尺度地理加权回归模型是两类多变量统计分析模型。其中,逻辑回归模型是用简单的线性回归来表达各评价因子之间复杂的非线性关系,计算便捷。地理加权回归模型本质是对普通线性回归方法的扩展,能描述自变量和因变量之间,在不同空间位置的不同关系。
双变量模型可揭示同一评价因子内各分级状态的相对重要性,但对不同评价因子间的重要性区分有限,而多变量统计分析刚好弥补这一问题,可构建多个自变量与一个因变量相关关系。回归模型可对多个评价因子进行综合分析,赋予每个因子不同的权重,但其基础是归一化的自变量值,而作为自变量的各评价因子种类多,且包括连续型和离散型,数值型和文本型数据,难以直接进行归一化处理,传统的专家打分法赋值又存在较强的主观性,所以为了提升评估成功率或准确性,本文综合各模型的优点,将两种双变量模型分别与两种多变量回归模型组合,首先依托ArcGIS分析灾点样本在各评价因子状态分级中的空间分布情况,然后采用双变量模型先对各评价因子状态分级进行权重计算赋值,也即完成了归一化,再通过多变量模型对归一化后的各评价因子指标与地质灾害的发生关联,计算各评价因子间的重要性差异,最终得到信息量—逻辑回归组合模型、证据权—逻辑回归模型以及信息量—多尺度地理加权回归、证据权—多尺度地理加权回归模型共4种组合模型。由此一定程度上解决了单一模型在地质灾害危险性评价中的不足,且能在GIS平台的支持下方便地实现可视化,具备较好的实践性和应用性。模型组合原理见图1。
平远县位于粤、赣、闽三省交界处,地理坐标东经115°43′ 41″ ~116°07′ 01″,北纬24° 23′ 38″ ~24°56′ 01″,县境总面积1381 km²。
平远县地质环境较复杂,人类工程活动强烈,存在较多方面的孕害条件和诱发因素,地质灾害频发。据平远县地质灾害详细调查报告分析,截至2016年平远县在册地质灾害隐患点中,共查明崩塌、滑坡和地面塌陷3类地质灾害隐患点503处。灾害类型以崩塌为主,滑坡次之。崩塌数量占比90.66%,滑坡数量占比9.15%。滑坡崩塌的失稳机制相似,具有相近的影响和诱发因素,故本文选取平远县2010—2017年期间发生的崩塌、滑坡,去除少量信息不完整的灾点后,以剩下的崩塌286处,滑坡92处,共378处灾点作为研究对象进行地质灾害危险性评价方法研究。取80%作为训练样本(302处),其余20%作为验证样本(76处)。
图1 双变量模型—多变量模型组合原理示意图Fig.1 Schematic diagram of principle of bivariate model-multivariable mode combination
图2 平远县位置示意图Fig.2 Geographical location of Pingyuan County
研究数据的精度及质量直接影响最终地质灾害危险性评价的结果,本文大量收集处理相关数据后,最终选用的数据及其来源如表1,其中本文使用的高程数据为NASA全球30 m SRTM高程DEM数据,距离数据是利用ArcGIS欧氏距离模块处理。
指标体系的建立是危险性评价的基础,主要包括评价因子分级、量化、筛选及建立评价模型。本文基于快速聚类法对连续型评价因子数据进行分级,基于双变量模型的指标量化,基于相关性分析进行筛选,最后通过多变量模型构建关系式,以降低主观性对指标体系建立的影响,同时保证各评价因子之间的相互独立性和各因子与地质灾害的相关性,进而提高危险性评价的准确性。
表1 各评价因子数据及来源Table 1 Data and sources for each evaluation factor
地质灾害是在多种条件和因素综合作用下发生的,因此在地质灾害危险性评价过程中,选取合适的评价因子是第一步也是最为基础的一步。主要包括孕灾环境和诱发因素两部分。本文结合滑坡、崩塌发生的内外因及研究区的地理地质特征,选取包括地形地貌、基础地质、水文环境、地表覆被的孕灾条件,以及包括气候环境、人类活动的诱发因素。得到最终的评价因子分级结果如图3。
地形地貌是崩塌、滑坡和泥石流等地质灾害产生的先决条件。斜坡的几何形态决定着斜坡体内应力的大小和分布,从而直接影响斜坡的稳定性与变形破坏模式。
平远县属丘陵山区,山地、丘陵占总面积超过70%,其余为河谷盆地。整体西北部高于东南部,形成北高南低的地势,坡度北陡南缓,局部亦有东陡西缓,海拔高度大多在200~800 m之间。
本文选取坡度、坡向、平面曲率、剖面曲率4个相关因子。
(1)地层岩性。地层岩性及岩性组合是直接指示斜坡岩土体“强度”的因素,基岩及堆积体的物理力学性质及其渗透性有所差异,直接影响坡体稳定性。它不仅影响区域滑坡、崩塌等的发育程度,同时可决定其类型及规模特征。
平远县地层复杂,少数乡镇有覆盖型可溶岩(岩溶发育),厚层易崩解的变质岩类、花岗岩类风化壳,第四系土层厚度大,不同区域不良地质体发育,境内出露的地层从老到新有震旦系(Z)、泥盆系(D)、石炭系(C)、二叠系(P)、侏罗系(J)、白垩系(K)、古近系(E)、第四系(Q)等,地层岩性包括白垩系下统优胜组(K2y)、侏罗纪晚侏罗世黑云母花岗岩(J 3 γ)、第四系全新统大湾镇组(Q h dw)等近30余类。
本文按照工程地质岩组分类进行后续统计分析。
(2)地质构造条件。地质构造条件对地质灾害发育的影响主要为:①通过影响地形地貌的形成进而影响地质灾害发育,在褶皱断裂附近的地形地势往往险峻,临空面发育,易发生崩塌等地质灾害;②通过改变岩土体的物理力学性质影响地质灾害的发育,一般在褶皱轴部和断裂带两侧,风化层厚,岩石破碎,裂隙发育,易发育灾害。与其他条件综合作用,使得地质灾害的分布在断裂构造附近越发密集。
平远县断裂构造纵横交错,在大断裂构造带的上下盘分布有大量的地质灾害点,在鹧鸪断裂、上举—猪麻坝断裂、长田圩断裂及中行—良畲断裂附近地质灾害点较多且展布方向与构造走向接近,一致呈长条形出现;在构造密集或交汇处,地质灾害点也密集且呈团块状分布。
本文选取距断层的欧氏距离来考虑地质构造活动对地质灾害的影响。
水对边坡稳定性的影响形式主要包括流水冲刷、软化作用、浮力减重和动水压力。一方面,河流水系对坡岸的侵蚀切割,易导致该部分岩土体各项性能降低,易失去平衡。另一方面,长期的流水作用影响周围边坡地下水情况,从而直接影响土体受力。故本文选取距河流的欧氏距离和流域沟壑密度两个相关因子。
沟壑密度表示单位面积内侵蚀沟(或水文网)的长度,它代表了一个地区河流密集程度,是表征内外营力对地表侵蚀影响的重要指标。本文利用ArcGIS水文分析模块基于平远县30 m分辨率DEM数据,按照小流域单元分析计算流域沟壑密度。
植被覆盖度主要影响地表水对岩土体的入渗侵蚀程度,长期或严重的水力侵蚀下,岩土体各方面性质受到影响,强度降低,进而导致边坡变形失稳概率增加。因此本文采用归一化植被指数(NDVI)来表征其特征。
自然因素是潜在内部因素,而不合理的人类工程活动则从外部加剧了地质灾害的发生和危害程度。近年来,随着社会经济的迅速发展和生活水平逐渐提高,削坡建房、修改扩建道路交通、兴建水利工程等人类工程活动难以避免地增多。据统计,截至2016年平远县由人类工程活动所造成的地质灾害点400处,占总数的78.7%。
本文选取距道路距离、距建筑物距离、土地利用3个因子来表征人类活动的影响。
降雨是地质灾害发生的主要诱因之一,主要通过软化、泥化、冲刷和增加静水压力、动水压力等形式直接破坏岩土体物理力学性质。高强度降雨和长时间降雨情况下,降雨迅速入渗导致渗流力增加和岩土体强度折减,从而导致坡体极易失稳。平远县处亚热带季风气候区,西北部山岭陡峻,河流落差大,流量受降雨影响,夏秋季雨多,流量充沛,遇长时间大暴雨,地质灾害频发。
本文采用2010—2015年间平均降雨量作为评价因子数据。
利用ArcGIS分析全部378处灾点样本在各评价因子分级状态中的空间分布情况,分别代入公式(2)~(4)。计算得出各分级状态的信息量I、证据权WoF值,结果见表2。
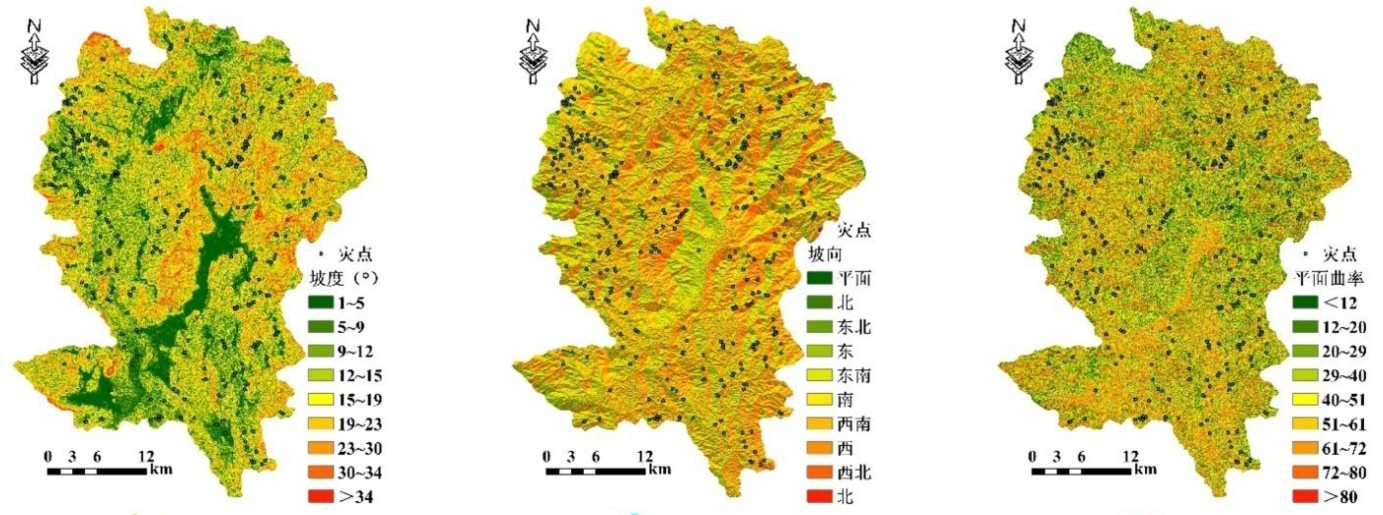
图3 各评价因子状态分级图Fig.3 The state classification diagram of each evaluation factor
表2 各评价因子状态分级及信息量(I)、证据权(WoF)值Table 2 The state classification of each evaluation factor,the information quantity(I)and weight of evidence(WoF)
变量之间的高度相关关系会使模型估计失真或难以估计准确性。逻辑回归分析需要以变量间不存在多重共线性为前提,因此首先需对各变量进行共线性诊断。本文选取灾点总样本的80%(即302个灾点)和302个未发生地质灾害的样本点作为训练样本,提取每个样本点的双变量模型值,采用SPSS软件中进行多重共线性诊断,一般认为所有自变量两两之间的Pearson相关系数>0.7,变量间可考虑存在共线性,方差膨胀因子VIF值>10,则表示存在多重共线性问题。经过逐次变量剔除后,表3中结果显示自变量之间相关系数均<0.3,且VIF值均<2,表明自变量间相关性较弱,可认为不存在共线性。
从结果可以看出,2种组合模型最终选出的评价因子不近相同,坡向和地层岩性因子只在IL组合模型中,而剖面曲率和流域沟壑密度只在WL组合模型中。
表3 评价因子相关矩阵及VIF值Table 3 The correlation matrix and VIF value of each evaluation factor
对通过筛选后的因子,采用SPSS进行二元逻辑回归,最终得到的结果如表4,显著性sig值均<0.05,说明组合模型通过检验。把结果中各评价因子的回归系数B作为该因子的权重β,常量为截距α,代入公式(6),利用ArcGIS进行栅格计算,即可得到每个栅格单元的危险性值。
从结果可以看出,三种组合模型最终的评价因子组成并不相同,且同一因子在2种组合模型中的权重也有区别。但权重大小排序变化不大。其中,距断裂距离、距道路距离几个因子在2种模型中权重都较小,排序靠后。
分别提取664个训练样本点的信息量I、证据权WoF模型值及经纬度坐标,并将是否发生地质灾害作为因变量(302个灾点样本赋值为1代表发生,302个非灾点样本赋值为0代表未发生),通过MGWR进行多尺度地理加权回归,并根据全局回归结果逐次剔除不满足显著性的因子,最终得到结果如表5,由于多尺度地理加权回归模型通常使用局部加权最小二乘方法进行逐点参数估计[11],得到的回归系数往往不是常量,而是随空间位置变化的变量,通过它的空间变化可以反映空间关系的非平稳性。故表5仅显示各评价因子回归系数的上下四分位数及平均值,可以看出各因子显著性值sig均<0.05,组合模型符合显著性检验。
表4 各评价因子逻辑回归系数Table 4 Logistic regression coefficients of each evaluation factor
根据4种组合模型得到的相应的指标体系,借助ArcGIS生成研究区地质灾害危险性概率分布图,在此基础上按照《地质灾害风险调查评价技术要求(1∶50 000)(试行)》要求,采用自然断点法对研究区进行危险性分级,划分为极高、高、中、低四个等级,结果如图4,可以看到所有模型下县域西北部都显示出较高的危险性,2类逻辑回归的组合模型的危险性分区结果大体相似,高危险区较为分散,主要在县域四周,而中部地区较多为低危险区。聚集性较大的高危险区包括西北方八尺镇,西边的中行镇。极高、高危险区与建筑物、道路密集地区重合度高的特征明显,符合平远县超过70%的地质灾害由修建公路、削坡建房导致的情况。2类多尺度地理加权回归模型的危险性分区结果也大体相似,但与逻辑回归模型的最终结果存在一定差异,针对平远县城区范围,基于逻辑回归模型结果为高危险性区,而基于多尺度地理加权回归模型的结果为低危险。而对于西北方八尺镇区域,都显示出较高的危险性,事实上这部分地区的地质灾害点分布也较为密集,为平远县防灾减灾工作应当重点关注的地区。总体上,基于逻辑回归模型的危险性分区较为分散和精细,而基于多尺度地理加权回归模型的分区更集中,呈团块状。
根据选取的378处地质灾害样本点,统计各危险性等级区域内地质灾害点分布情况如表6,4种组合模型下落入极高危险区的比例分别达到72.487%、 82.011%、 82.011%、 73.545%,而落入低危险区的灾点比例都低于6%,其中证据权—逻辑回归和信息量—多尺度地理加权回归组合模型的极高危险区灾点比例为82.011%,低危险区的灾点比例为1.323%。显示出较优的综合效果。
表5 各评价因子多尺度地理加权回归系数Table 5 MGWR coefficients of each evaluation factor
从前述危险性评价结果分析看来不同组合间结果有一定区别,为更好地检验和对比各组合模型的评价结果的可靠性,本文依据未参与模型训练的76个灾点样本和76个随机选取的未发生灾害的样本点,通过3种方法对不同组合模型进行精度评价。其中,Cohen′s Kappa系数法属于典型的受临界值约束的精度评价方法,其优点在于计算简便。ROC曲线法是目前普遍使用的不受临界值约束的精度评价方法,它通过连续的关系曲线下的面积来表征效果好坏,不受临界值的约束,较客观有效。Sridevi Jadi经验概率法则介于前两者之间,本质上也属于受临界值约束的评价方法,但不同于Cohen′s Kappa系数法的是其临界值不唯一。
图4 各组合模型地质灾害危险性评价结果图Fig.4 The results of geological disaster risk assessment of each combined model
表6 各组合模型地质灾害危险性分区灾点分布情况Table 6 Distribution of disaster points in geological hazard zonings of each combination model
Kappa系数属于Heidke技术得分法,验证时设定一个临界值,将实际值和评价结果进行二分类。计算即可得Kappa系数[12]。
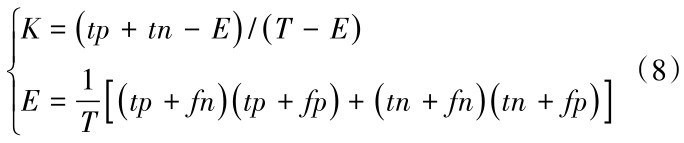
式(8)中,T为单元总数,其他各参数见表7,认为K>0.61评价模型精度较好,0.41≤K≤0.60时精度中等,K<0.4时精度较差。
基于二分类,Sridevi Jadi提出了以经验概率为表达方式的精度评估方法[13],其计算公式为:

式(9)中,N是单元总数,S是存在灾点样本的单元数;M是危险性等级为极高和高的单元数;MS是存在灾点样本的危险性等级为极高、高的单元数。4.2.3 ROC曲线法
受试者操作特性(Receive Operation Characteris⁃tic,ROC)曲线,是对各模型的危险性评价结果,取若干不同的临界值得到不同的真阳性率(True Positive Rate, tp)和假阳性率(False Positive Rate, fp),见表7 。为了定量比较,一般以真阳性率为纵坐标,假阳性率为横坐标绘制的曲线,使用曲线下面积(Area Under Curve,AUC)作为定量指标来评价其精度。ROC曲线上的点代表采用不同临界值创建的列联表对(fp, tp)。ROC曲线越靠近左上角,意味着AUC值越大,则对应的模型性能更优。
表7 精度评价列联表Table 7 Contingency table of accuracy tests
由表8可以看出基于多尺度地理加权回归模型的组合模型的评价结果精度普遍低于基于逻辑回归组合模型的结果,可见尽管地理加权回归模型在地质灾害危险性评价方面具有一定的创新性,也在一些地区的应用上取得了较好的效果,但是针对本文的研究区广东省平远县,并不具有很强的优势,可能是因为平远县境内主要是低山丘陵,各因子数据精度有限,区域内地层岩性、土壤类型等显示出同类型大范围成片分布,导致空间异质性较小,样本量较小也一定程度影响了地理加权回归的结果。
表8 各组合模型危险性评价精度检验对比Table 8 Comparison of accuracy test of risk assessment for each combined model
两种逻辑回归组合模型的评价结果精度指标差别很小,证据权—逻辑回归组合模型,在运用Cohen′s Kappa系数和Sridevi Jadi经验概率法计算的精度均更高,而从ROC曲线图(图5)看,精度则略低于信息量—逻辑回归组合模型的0.869。综合结果分析表6中所有灾点样本落入极高和高危险区的比例,证据权—逻辑回归组合模型下,比例高达94.445%,高出信息量—逻辑回归组合模型下的87.566%较多,本文认为证据权—逻辑回归组合模型的结果相对更优。
图5 各组合模型ROC曲线Fig 5 ROC curve of each combined model
本文通过采用信息量—逻辑回归组合模型、证据权—逻辑回归模型以及信息量—多尺度地理加权回归、证据权—多尺度地理加权回归模型共4种组合模型,依托广东省平远县2010—2017年的主要地质灾害(滑坡、崩塌)进行危险性评价。结果表明:
(1)从精度分析结果看,基于多尺度地理加权回归模型的组合模型的评价结果精度普遍低于基于逻辑回归组合模型的结果,2种逻辑回归组合模型的评价结果精度差别很小,综合结果分析所有灾点样本在危险区的分布情况,以及3类精度分析方法结果,认为证据权—逻辑回归组合模型的结果更合理和适用。尽管多尺度地理加权回归模型在地质灾害危险性评价方面具有一定的创新性,但是针对本文的研究区广东省平远县,并不具有很强的适用性。
(2)从证据权-逻辑回归组合模型的危险性分级结果可见,平远县地质灾害高危险区主要在县域四周,而中部较多为低危险区。聚集性较大的高危险区包括西北方八尺镇,西边的中行镇。极高、高危险性区域沿建筑物、道路密集地区分布的特征明显,对应平远县超过70%的地质灾害由修建公路、削坡建房导致的情况,可见评价结果具有一定的可靠性。
此外,本文直接选取滑坡、崩塌两类地质灾害作为对象,开展区域地质灾害危险性评价,是基于平远县在册地质灾害以滑坡崩塌为主,且两类灾害的孕灾环境和诱发因素基本相同的实际情况。与对两类灾害分别进行分析相比,既有其操作性强的优势,也存在一定的局限性。其次,文中采用的地质灾害样本数量有限,而研究区的面积较大,物理力学模型的应用受限,且统计分析方法对灾害机理考虑不足,尤其无法反映时间尺度下降雨因素的影响,也导致所得结论可能存在一定的局限性,针对高危险性小区域应该选择基于物理力学分析的边坡稳定性计算方法作进一步研究。