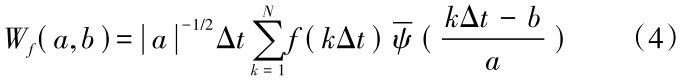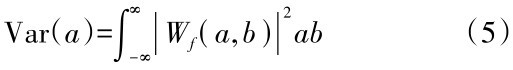4.1 时间上的响应
震级反映着地质运动的强烈程度,是由地震仪测定的每次地震活动释放的能量多少来确定,在我国以国家地震台网测定的数据为准。一般来说,地震震级在5.0级以上可能会对地表造成影响,6.0级及以上地震可能会产生崩塌和滑坡。一般来说,震级越高,产生烈度就越大,对山体的损失就更为严重,产生松散物源就越多,在降雨的诱发下发生泥石流的概率就越高。但地震影响泥石流在时间上的长度及周期性仍不明确,需进一步研究。
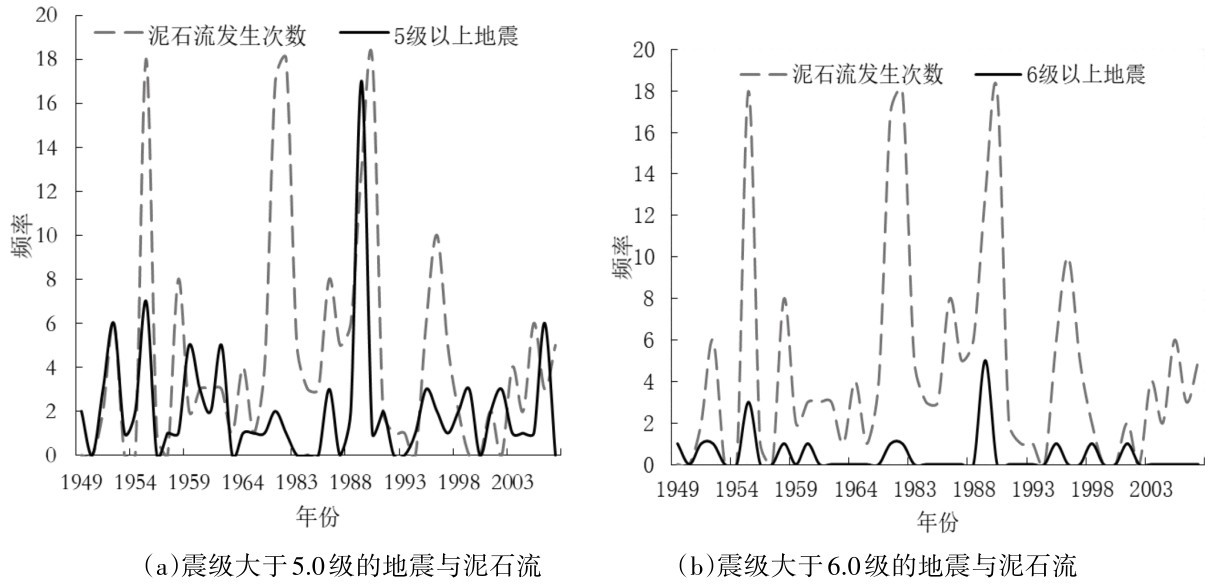
通过将震级大于5.0级、震级大于6.0级的地震分别与泥石流的发生频次进行直观对比分析(图2),发现泥石流与地震活动均具有一定的周期性,震级大于5.0级的地震发生频次有12个波峰,震级大于6.0级的有6个波峰,泥石流的发生频次共有12个波峰。经分析可知,当地震的发生频次有波峰时,泥石流在该时段同样存在波峰;地震发生频次波峰高时,泥石流发生频次的波峰相应增高,且泥石流发生频次的截距要比地震的略大,其中在震级大于6.0级的地震中更为明显,表明地震发生频次高时,泥石流发生频次也相应变高。在1959—1964年期间,发生5.0级以上地震时,泥石流也集中发生,且发生频次相应变高。对比1964—1983年与1988—1993年两时段,1964—1983年地震发生频次的峰值虽然不高,但与1988—1993年段泥石流的基本相似,原因是1973年2月6日,四川炉霍县发生7.6级地震,震级的放大效应导致了泥石流的响应增强;部分时段泥石流波峰出现了延后效应。
综上可知,地震与泥石流活动有一种关联性,即地震发生频次影响泥石流发生频次,一般地震在1~3a内具有强烈的影响作用,震级越高,对泥石流发生影响越明显,特别震级达6.0级以上时较为明显,高震级放大效应导致泥石流响应增强,泥石流的发生周期与地震发生周期具有趋同性。
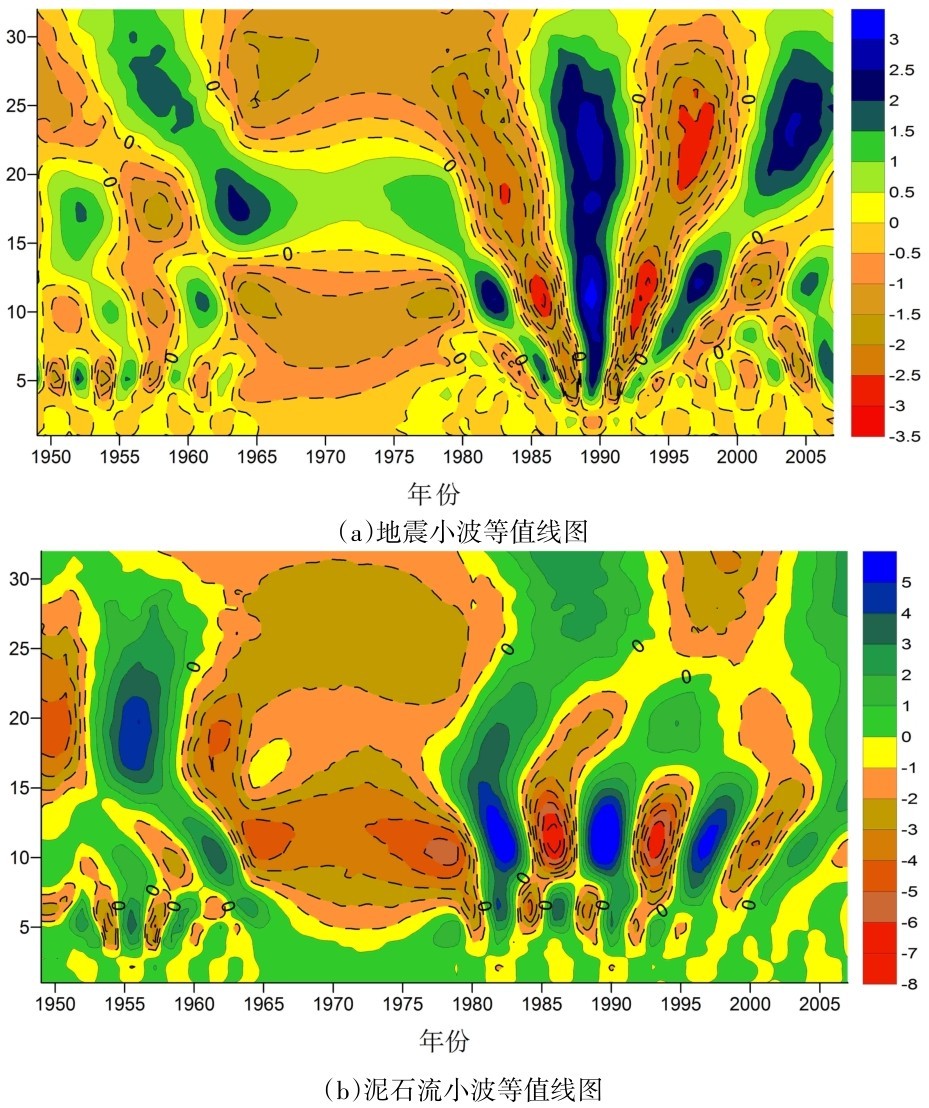
小波系数实部等值线图能反映数据时间序列在不同时间尺度的周期变化及其在时间域中的分布,进而能判断其在不同时间尺度上的发展过程及其趋势,可进一步验证地震和泥石流的周期性。如图3所示,它分别反映出地震、泥石流在不同时间尺度的发生频次变化及其在时间范围及突变点分布。其中,当小波实部值为正时,代表着泥石流及地震发生频次为高峰期,在图中用实线绘出,蓝色部分代表着发展较大,颜色越深发生频次越高。当小波实部值为负时,说明为泥石流与地震发生的低谷期,红色部分代表着频次的最低值,颜色越深发生频次越低。等值线的疏密分别对应指标的偏少和偏多时期。在等值线实线与虚线相交的地方,标记为0。
图2 地震与泥石流的发生频次分布Fig.2 Frequency distribution of earthquakes and debris flows
图3 地震、泥石流小波系数实部等值线图Fig.3 Real part contour map of wavelet coefficient of earthquake and debris flow
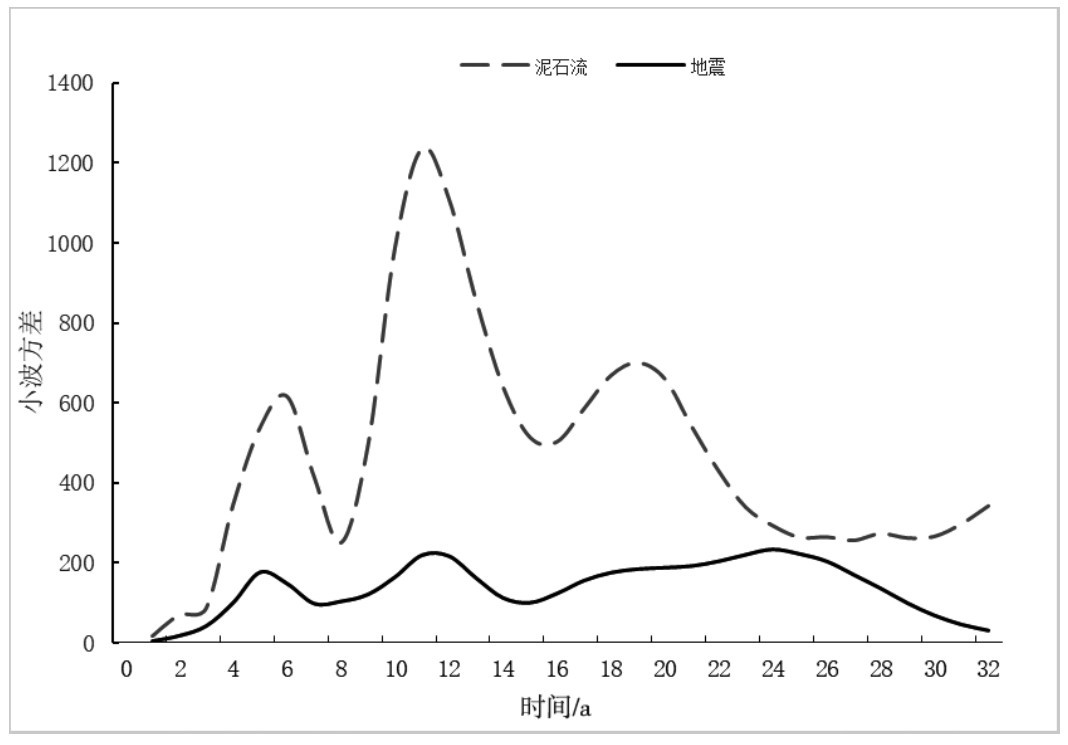
由此可知,地震小波一共存在3~8 a、8~14 a、14~28 a三类尺度的周期变化(图3a)。在3~8 a时间序列中,存在10个准周期震荡,代表着小尺度的变化,其中在1982—1990年等值线比较密集反映其的周期性较强;在8~14 a时间序列中,存在6个准周期震荡,代表中尺度的变化,其中在1981—1999年周期性较强;在14~28时间序列中,存在3个准周期变化,代表着大尺度的变化,其中在1980—2003年周期性较强。综上表明,小尺度的增减变化受到大尺度的增减结构变化控制,并且地震小波方差随时间尺度变化的过程有3个较明显峰值,分别对应着5 a、12 a、25 a(图4),因此地震发生频次在5 a、12 a和25 a分别存在主周期。泥石流小波等值线图也存在三类周期变化,分别是4~8 a、8~14 a、14~25 a(图3b),其中,4~8 a有8个准周期震荡,为泥石流小尺度变化;8~14 a有5个准周期震荡,为中尺度变化;14~25 a有2个准周期震荡,为大尺度变化。泥石流小波方差在时间尺度变化的过程中在7 a、11 a、20 a时有明显的波峰,表明它们在相应尺度下信号震荡强烈,所以泥石流发生年频次在7 a、11 a和20 a存在3个主周期(图4)。
通过小波分析可知,泥石流发生周期在小尺度内比地震发生周期多1 a,在中尺度周期相同,在大尺度时比地震周期长7 a。说明泥石流在不同尺度的周期等于或大于地震周期,在大时间尺度影响下泥石流发生周期要比地震发生周期长,表明泥石流的活跃周期相比地震发生是一个持久的过程,地震发生影响泥石流活跃周期可达1~7 a,所得结果高于直观分析。通过对不同时间尺度下的地震与泥石流准周期震荡的对比,地震震荡周期频次均比泥石流震荡周期频次更高,意味着泥石流的暴发未必是一次地震而引起的,可能是多次地震下以及降雨等多种因素影响下的结果。
图4 地震、泥石流暴发次数小波方差分布Fig.4 Wavelet variance distribution of the outbreak times of earthquakes and debris flows
4.2 空间上的响应
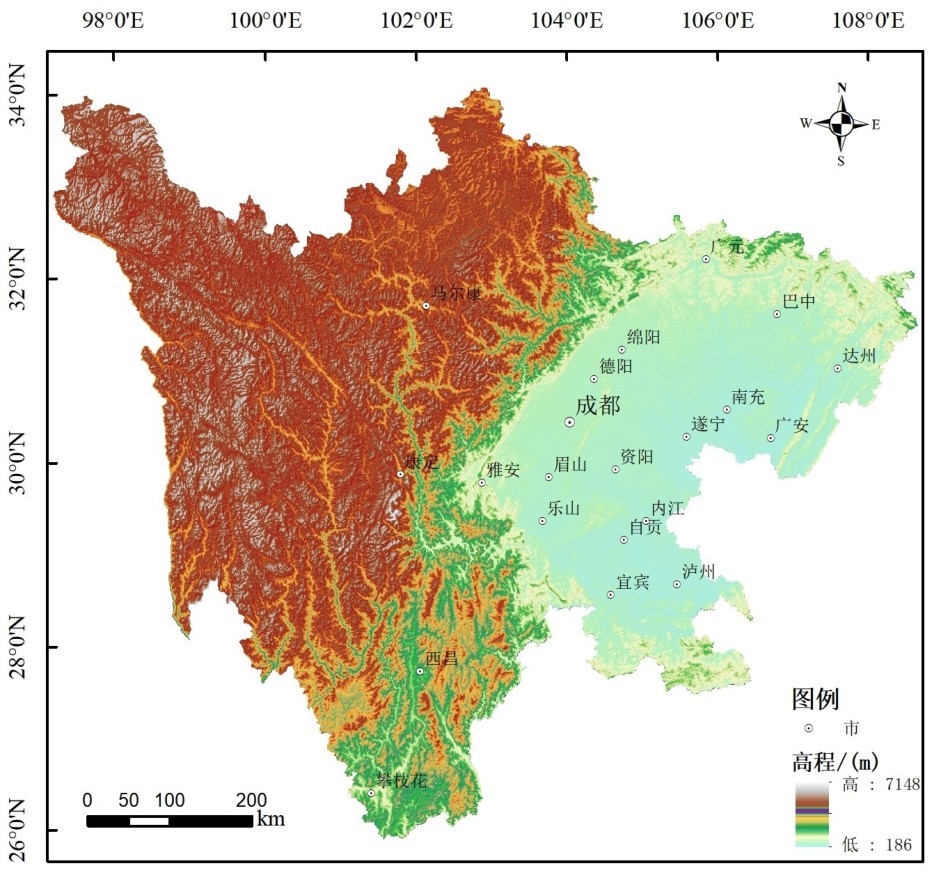
全球上大部分崩塌、泥石流、滑坡等山地灾害分布在欧亚地震带和环太平洋火山地震带这两大地震带上[19]。因此,在一定程度上地震带或构造活跃带也就是泥石流活跃带。在我国已划分出的23个地震带中,有16个地震带就是泥石流活动带,占地震带总数的69.6%。其中以安宁河谷带、腾冲—澜沧带、康定甘孜带、西藏察隅带、武都—马边带、滇西带泥石流最为发育。我国四大泥石流灾害区(藏东南地区、陇南地区、川西北山地、云南小江流域)中除藏东南位于欧亚地震带上,其余3个地区基本位于我国东西分界线附近的南北大地震带上。由于印度板块、菲律宾板块、太平洋板块分别与亚欧板块相碰撞,在中国内陆形成各自连续变化的应力场,在104°E线附近形成一个南北延伸应力变化不连续的地区。这个带上虽无巨大现代构造山系,但新构造运动强烈,地震活动频繁,同时也是泥石流、滑坡、崩塌等山地灾害强烈作用带[20]。活动断层是地震形成的主要因素,地震等级直接体现地震能量的大小。一般来说,距震中越近,地震破坏的规模越大,地震烈度则体现地震对地表的影响及破坏程度。鉴于此,采取断裂带密度、地震震级、距震中距离和地震烈度4种地震指标与泥石流空间上的分布关系进行分析。
4.2.1 断层密度对泥石流分布的影响
利用ArcGIS软件对断裂带进行线密度分析,得出断裂带密度为0~0.829条/km2,结果重分类后利用自然分割分为5个等级,并转换为矢量文件与泥石流点进行求交运算得出泥石流点与断层密度之间的关系。由图5可知,大部份泥石流灾害点与断裂带空间分布呈近似平行关系。根据泥石流灾害数量和灾害密度状况分析,泥石流在断裂带密度等级为4时最多,等级为2时次之。除断裂带密度等级为5外,呈断裂密度越低泥石流灾害数量越低的趋势。泥石流密度在断裂带密度等级为4时最高,等级为5时次之,说明泥石流在断裂带位置处发生不是最强烈,而是在其相近区域内,基本呈断裂带密度越大、泥石流灾害密度越高的趋势。综上,泥石流发育数量与断裂带有在空间位置上具有呈与近似平行关系,表现为距断层带越近、泥石流灾害越多的特征。
4.2.2 震级对泥石流分布的影响
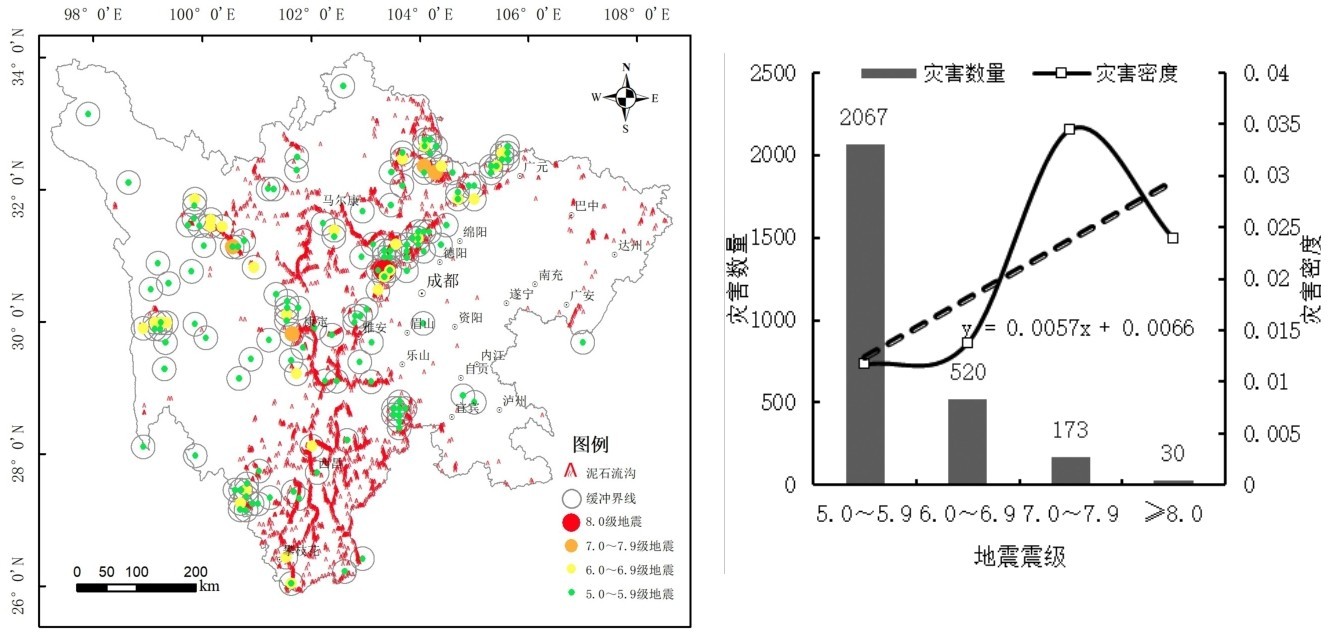
通过ArcGIS对5.0~5.9、 6.0~6.9、 7.0~7.9、≥8.0级地震以20 km为距离进行缓冲处理,求交运算得出范围内地震震级与泥石流分布上的关系,如图6所示。根据泥石流灾害数量和灾害密度状况分析,泥石流发生在地震5.0~5.9级范围内最多, 6.0~6.9级次之,基本随地震震级上升而下降趋势。从空间表现来看,泥石流分布总体与高震级呈带状分布,在龙门山断裂带、安宁河谷断裂带等地区,地震对泥石流的影响较高;在川东北的巴中、广元地区,因地震发生频次低,地震规模小,对泥石流的影响较低。泥石流分布密度在5.0~6.9级较低,≥7.0级较高,其中7.0~7.9级地震影响下的泥石流密度最高。综上可知,泥石流发育数量与震级有很大关系,震级主要影响泥石流发育的密度,震级越高,泥石流密度越高。
图5 断层密度与泥石流的空间分布关系Fig.5 Spatial distribution relationship between fault density and debris flow
图6 震级与泥石流的空间分布关系Fig.6 Spatial distribution relationship between magnitude and debris flow
4.2.3 震中距离对泥石流分布的影响
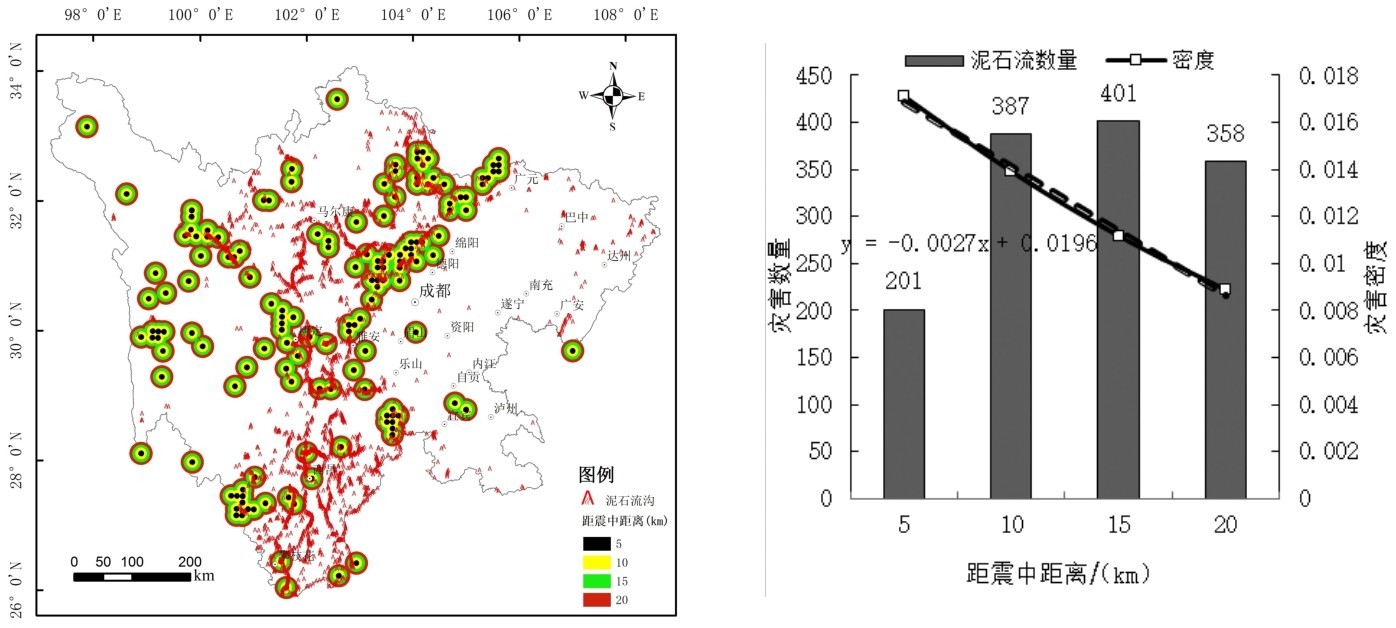
以地震震中为中心、 5 km为单位进行缓冲,共分为4级,分别为5 km、10 km、15 km、20 km,并通过求交计算可知缓冲距内部的泥石流密度。由图7可知,除川西地区部分高原夷平面泥石流较少发育区及川东北地震较少发生区,其余地区泥石流灾害基本沿地震高发区成片分布,且随距地震震中距的远近不同,分布密度不同。泥石流活动主要在距震中5~15 km处。根据灾害密度分析,随着距震中越远,泥石流密度越小,呈线性负相关。
4.2.4 地震烈度对泥石流分布的影响
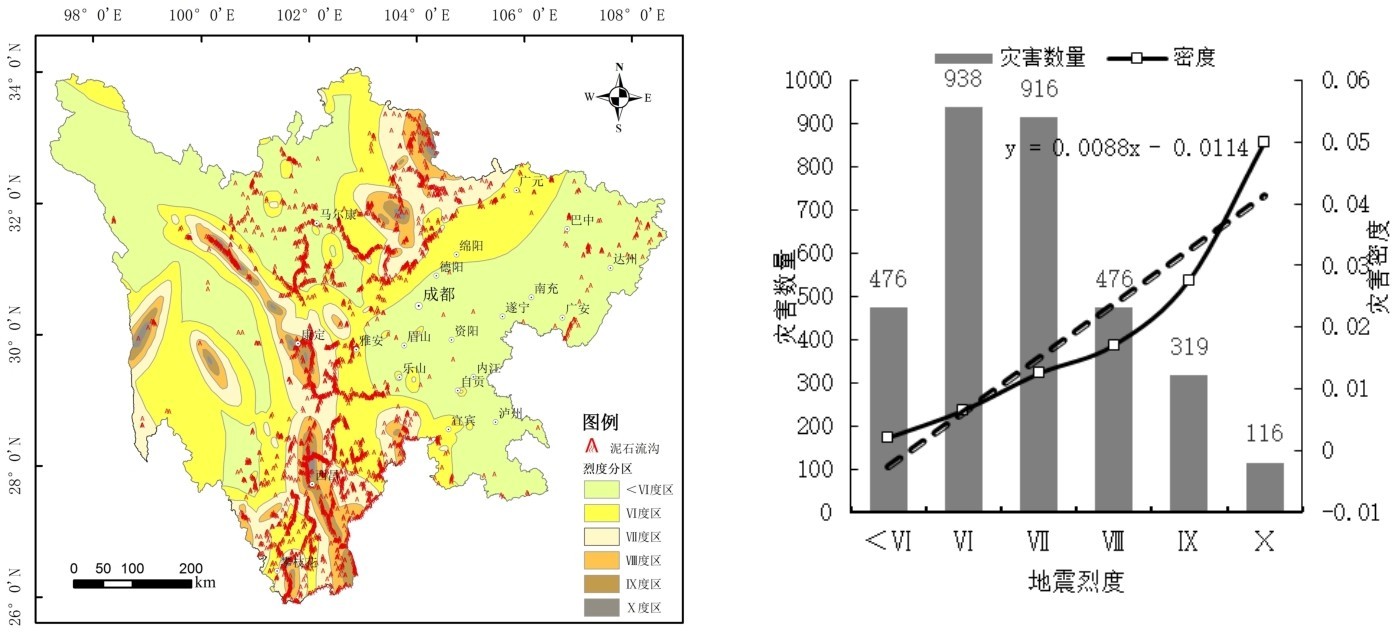
利用ArcGIS对地震烈度分区与泥石流灾害点进行求交运算,可以得出地震烈度与泥石流灾害点的密度及空间分布情况(图8)。根据泥石流灾害数量和灾害密度状况分析,泥石流灾害在烈度Ⅵ度范围内最多,Ⅶ度次之。除<Ⅵ度范围外,基本随地震烈度上升而呈下降趋势。泥石流密度在<Ⅵ度最低,Ⅹ级泥石流密度最高。因此,泥石流发育数量与烈度总体呈线性正相关,说明烈度越高时泥石流发育的密度越高。
综上所述,将断裂带密度、地震震级、距震中距离、地震烈度与泥石流密度关系通过二元一次方程组曲线拟合,设其比例系数为k,得知其k值的绝对值在0.0012~0.0088之间,结果较为相近,说明采取的4种因子在与地震关系上具有相似性,其共性可以代表地震与泥石流的空间关系。从空间分布来看,泥石流与地震的空间分布成带(条)状集中分布,距地震因子越近,泥石流灾害密度越高,其比例系数平均为0.0034。
图7 震中距与泥石流的空间分布关系Fig.7 Spatial distribution relationship between epicenter distance and debris flow
图8 地震烈度与泥石流的空间分布关系Fig.8 Spatial distribution relationship between seismic intensity and debris flow

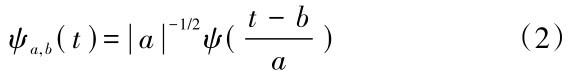
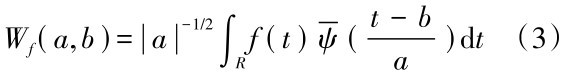
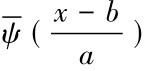 为
为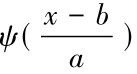 )的复共轭函数。由于得到的时间序列数据往往为离散形式,设函数f(k Δt),(k=1,2,…,N;Δt为取样间隔),则式(3)的离散小波变换形式为:
)的复共轭函数。由于得到的时间序列数据往往为离散形式,设函数f(k Δt),(k=1,2,…,N;Δt为取样间隔),则式(3)的离散小波变换形式为: