DOI: 10.13512/j.hndz.2023.02.02
备注
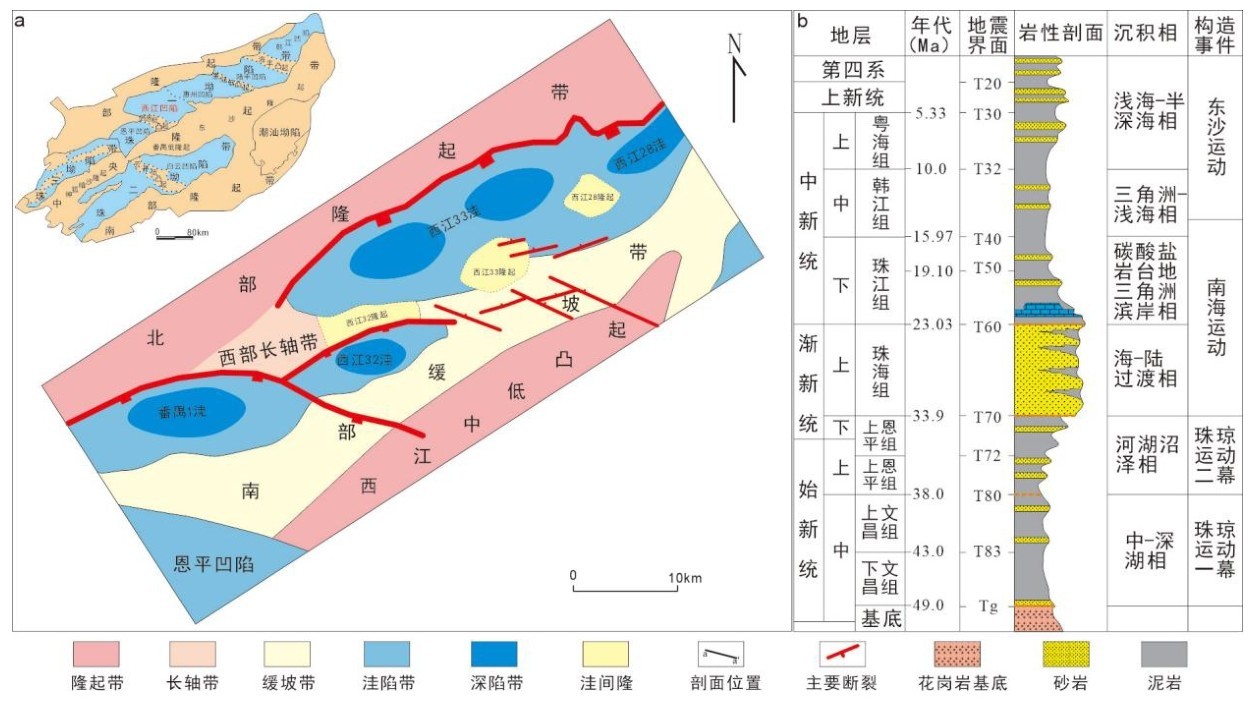
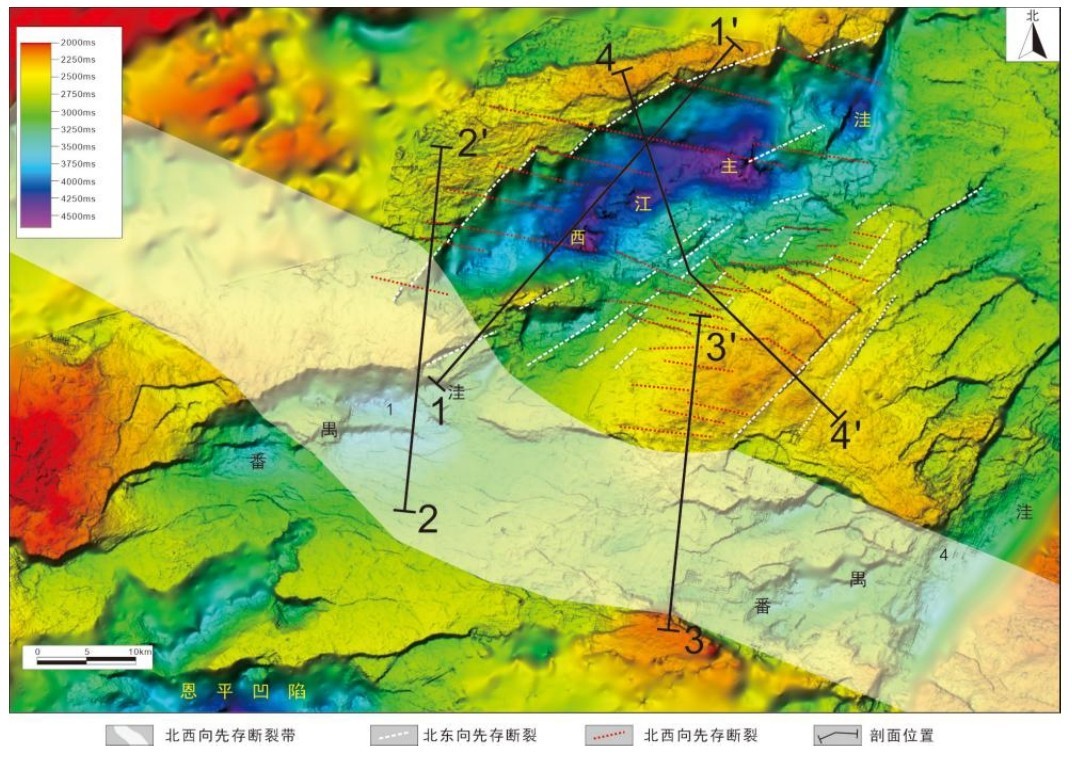
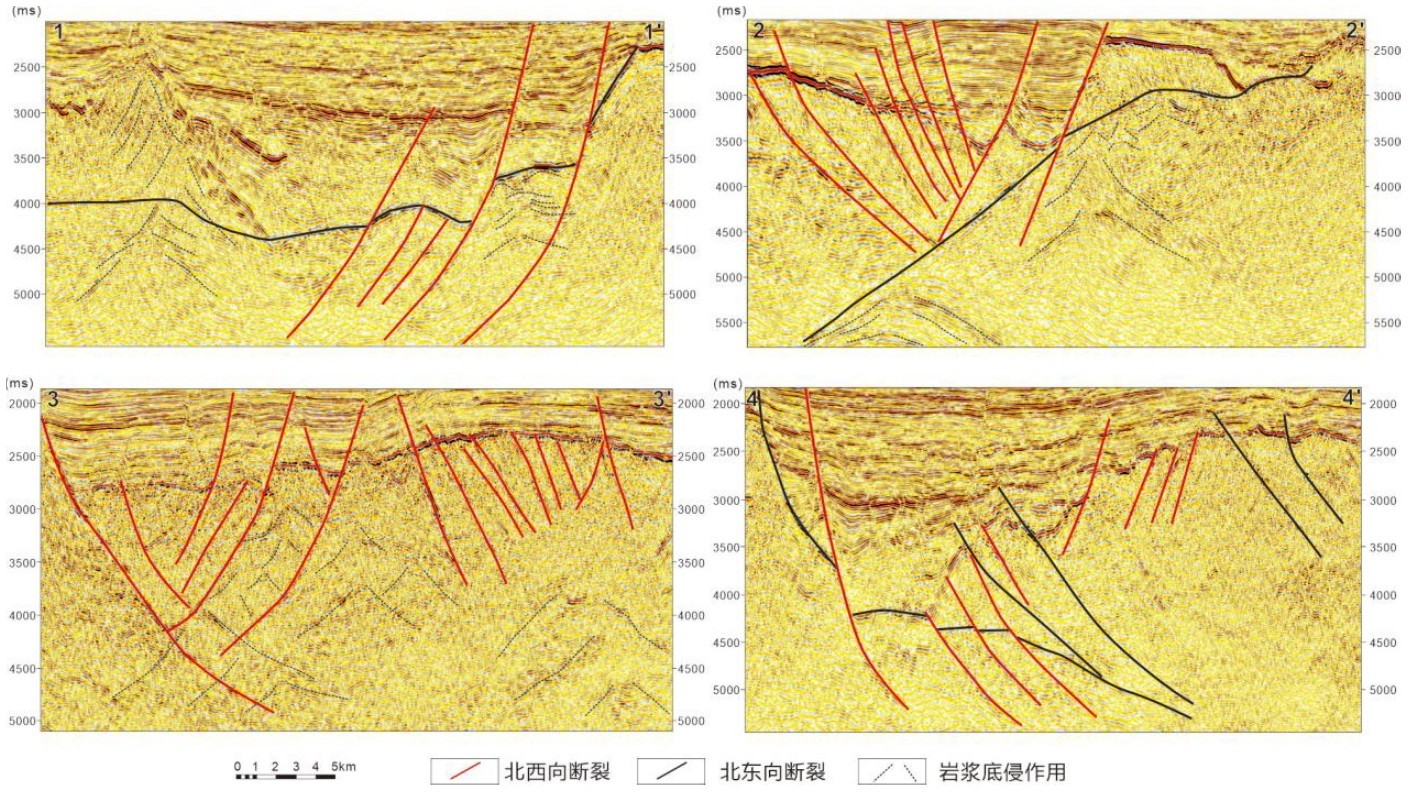
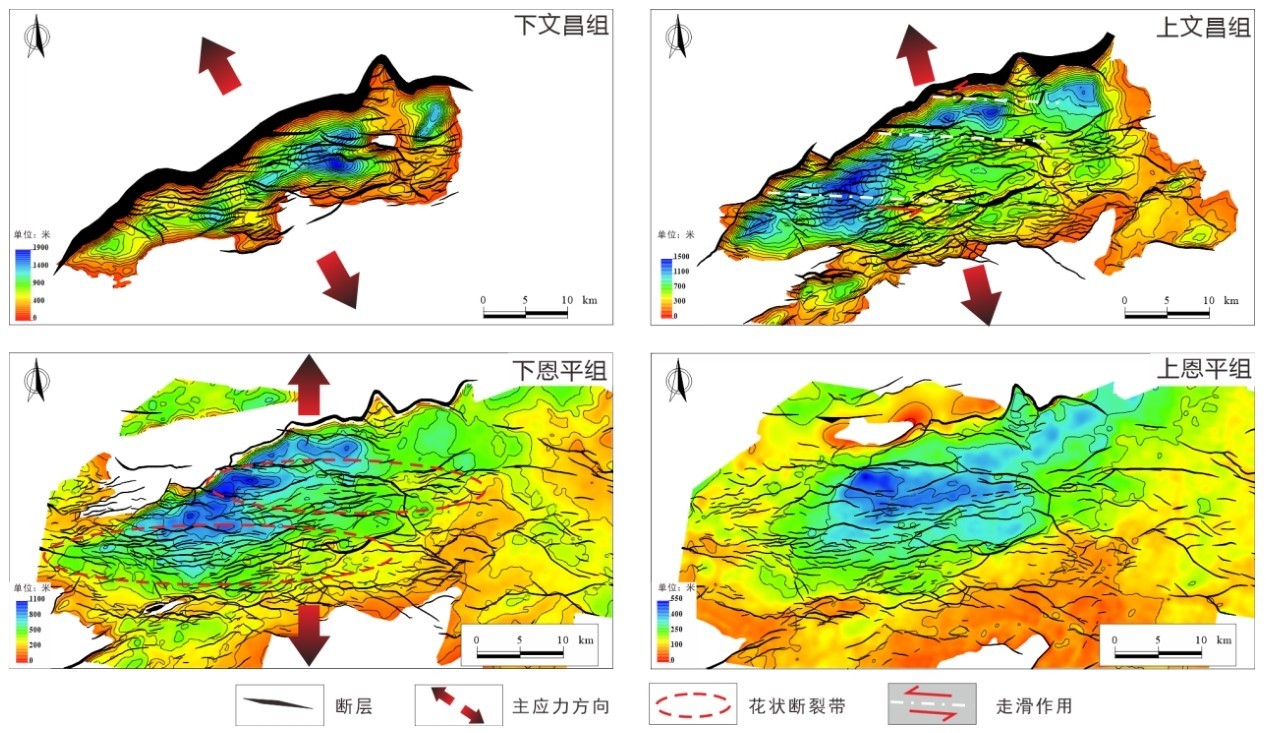
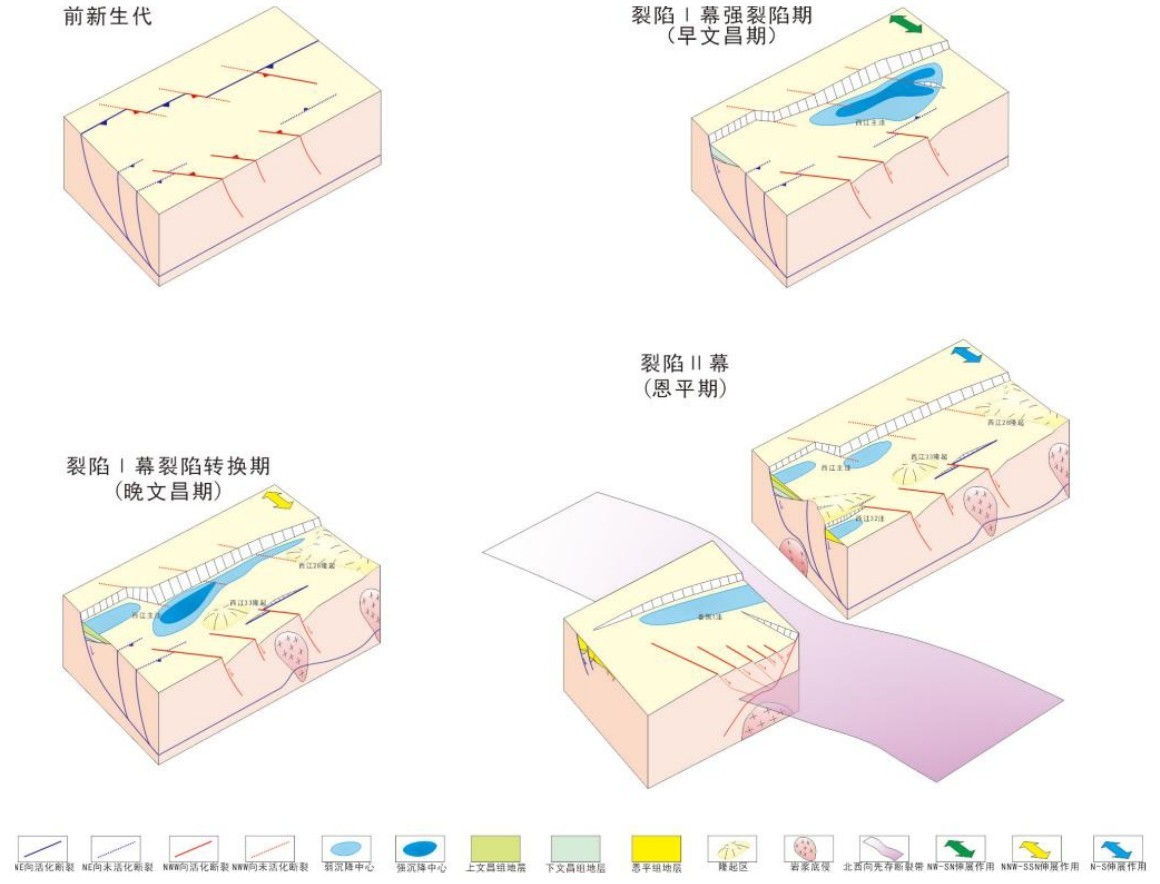
先存断裂体系的差异活化对西江主洼的成盆作用影响显著,进而控制烃源岩的分布。此次研究依托三维地震资料,在西江主洼地区开展先存断裂体系的识别及划分,从盆地动力学角度,分析先存断裂体系在伸展应力场下的差异活化对西江主洼成盆演化的控制作用。在西江主洼地区识别出北东向和北西向两组先存断裂体系,北东向先存断裂规模较大,呈北缓南陡分布特征,早文昌期优先活化并控制洼陷基本格局,北西向先存断裂晚于北东向先存断裂形成,规模小,分布广,研究区范围呈西密东疏分布特征,在西江主洼以西构成北西向先存断裂带,控制洼陷区晚文昌期之后的构造迁移;建立西江主洼受应力场动态转变控制的迁移型成盆演化模式:裂陷Ⅱ幕裂陷作用减弱,继承性发育宽缓半地堑,明确西江主洼有利烃源岩发育的区域构造背景。
The differential activation of the pre-existing fault system has a significant influence on the basin formation of the Xijiang Main Sag, and then controls the distribution of hydrocarbon source rocks. Based on 3D seismic data,this study carried out the identification and division of pre-existing fault system in the Xijiang Main Sag, and analyzed the control effect of differential activation of pre-existing fault system under extensional stress field on the basin-forming evolution of the Xijiang Main Sag from the perspective of basin dynamics. Two groups of pre-existing fault systems with NE and NW directions have been identified in the Xijiang Main Sag. The NE trending pre-existing faults are large in scale, characterized by slow distribution in the north and steep distribution in the south. They were preferentially activated in the early Wenchang period and controlled the basic pattern of the sag. The NW trending pre-existing faults were formed later than the NE trending pre-existing faults, with small scale and wide distribution. The study area is characterized by dense distribution in the west and sparse distribution in the east. The NW trending pre-existing fault zone is formed in the west of the Xijiang Main Sag, which controls the tectonic migration of the sag area after the late Wenchang period. A migration-type basin-forming evolution model controlled by the dynamic transformation of the stress field in the Xijiang Main Sag is established: The split half-graben in the first episode of the rift migrated westward from the "narrow-deep type" to the " flexural type", the rifting in the second episode is weakened,and the inheritance of the wide and gentle half graben is developed. The regional tectonic background of favorable hydrocarbon source rock development in Xijiang Main Sag is clarified.