基金项目:山东省地震局一般科研项目(YB2011)
作者简介:郑旭(1990-),男,硕士,工程师,研究方向:地震动衰减关系。E-mail:zhengxu0110@163.com
通信作者:周少辉(1991-),男,硕士,工程师,研究方向:数字地震。E-mail:674891062@qq.com
1.Shandong Institute of Earthquake Engineering , Jinan 250021, China;2.Shandong Earthquake Agency , Jinan 250014, China
Manila Trench;Sbduction zone;Plate margin earthquake;Attenuation relationship
DOI: 10.13512/j.hndz.2022.01.12
俯冲带是由陆地板块与海洋板块或者海洋板块之间通过俯冲作用[1]形成的地质构造复杂,地震活动频繁的区域。根据板块俯冲角度、岩石层厚度以及震源深度等因素,俯冲带地震包含板内、板缘地震两种类型。板缘地震通常是浅角插入事件,震源深度一般为15~50 km[2],如发生于智利1984年Valpariso8.0级、 2014年西北部海域8.2级地震及2003年日本东北部俯冲带8.1级地震等。在中国南海海盆东侧,菲律宾板块俯冲至欧亚板块后形成了一条南北方向弧形西凸的俯冲带,即马尼拉海沟俯冲带,全长约1000 km,位于118°~123°E, 12°~22°N之间[3]。按照活动构造分类,板缘活动构造分为汇聚型、离散型及转换型活动构造[4],马尼拉海沟俯冲带位于南海海盆与菲律宾群岛边界,属于汇聚型活动构造,由于板块之间俯冲作用,该区域以逆断层为主。
目前,俯冲带地震的研究主要集中在美国西部Cascadia地区俯冲带、日本东北部俯冲带、台湾东北部俯冲带等,在中国南海区域,由于港珠澳大桥等重大近海交通工程的建设,马尼拉海沟、琉球海沟等俯冲带地震的研究也有了一定的进展[5]。对俯冲带板缘地震的研究,Atkinson[6]采用随机有限断层模型模拟了Cascadia俯冲带矩震级7.5~9.0级的板缘地震时程和反应谱;Si Hong Jun[7]在统计了日本东北部俯冲带20余次地震数据后得出,板缘地震的地震动效应要大于浅地壳及板内地震;Atkinson等[8]通过上千条5.0~8.3级的俯冲带板缘、板内地震记录的分析指出,板缘地震在震级为8.0级左右时,要考虑300×500 km的矩形地震危险区域;郝彦春[9]以2003年9月26日日本东北部俯冲带8.1级地震及2014年4月1日智利8.2级地震作对比,得出俯冲带板缘地震存在高频衰减及90%能量持时随着震中距的增加而增长等现象;胡进军等[10]通过日本东北部俯冲带地震与汶川、庐山等浅地壳地震相比较得出,俯冲带板缘地震PGA随距离衰减速率慢于板内地震及浅地壳地震。
对于俯冲带地震动衰减关系的研究,Youngs [11]以日本、美国、智利以及墨西哥等国家的俯冲带记录为基础,建立了俯冲带板缘地震动衰减关系,并应用到地震动加速度峰值的预测中;Chang[12]等利用台湾地震动加速度记录建立了台湾东北部俯冲带及地震动活跃的浅地壳地震动衰减关系,提高了地震动预测的准确性;Lin等[13]以台湾东北部俯冲带板缘地震记录为基础,建立了该俯冲带板缘地震峰值加速度及反应谱的衰减关系;在南海俯冲带的研究中,胡进军等[14]建立了基于混合方法的南海俯冲带板内地震动衰减关系。
综上所述,对于俯冲带板缘地震的特点及衰减关系的研究已有一定的成果,但是特殊的地理位置决定了在俯冲带地震近场区建立台站来记录地震波形数据较为困难,因此直接采用实际数据来系统研究板缘地震动仍有很长的路要走。面对这一问题,在分析马尼拉海沟俯冲带地质构造及类比其他区域板缘地震的前提下,通过数值模拟数据来分析俯冲带板缘地震动特点并探讨板缘地震动衰减规律将是有效的方式。
马尼拉海沟位于南海海盆东侧,由菲律宾板块俯冲至欧亚板块以下形成。据史料记载,该俯冲带发生过多次震级大于4.5级的破坏性地震。图1给出了马尼拉海沟所在区域(10°~25°N,110°~125°E)的历史地震震中分布,其中,震级在5.0~6.9级之间的地震占比较大,并发生了数次震级大于7.0级的强破坏性地震,且海沟北段的地震频次要明显大于南段,因此,马尼拉海沟对南海海域及中国东南沿海地震灾害所产生的影响不容忽视。
图2给出了马尼拉海沟所在区域震级大于4.5级的历史破坏地震震源深度三维分布图。图中可以看到,震源深度在0~50 km范围内不间断分布, 15~50 km之间,随震源深度增加,地震频次有逐渐增加的趋势。从位置来看,主要集中在马尼拉海沟及其东侧,说明该区域的地质和构造满足地震易发多发的条件。
图1 历史破坏地震震中分布Fig.1 Epicenter distribution of historical destruction earthquakes
图2 历史破坏地震震源深度分布Fig.2 Depth distribution of historical destruction earthquakes
图3 历史破坏地震M-t图Fig.3 M-t diagram of historical destruction earthquakes
图3展示了自1901年以来,发生于马尼拉海沟及其附近海域震级大于4.5级的破坏性地震的时间分布。图中可以看到,自1901年以来,该区域破坏性地震发生次数按时间分布比较均匀,且每10年左右会发生一次震级大于7.0级的地震,地震活动性强,破坏性大。
鉴于无法直接用该俯冲带地震数据来分析板缘地震动及其衰减规律的状况,本文采用随机有限断层模型[15]来模拟发生于马尼拉海沟俯冲带的地震,分析地震动特点并探讨地震衰减特征。
随机有限断层法是将震源所在断层划分为N个子断层,每个子断层看作点源,地震发生后,以一定的破裂速度向外辐射传播,每个子断层对场点有差异的贡献经过叠加即可得到所求场点的地震动,该过程可以公式(1)来表示
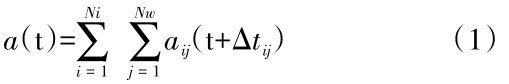
式中,a ( t )表示子断层地震动加速度。
模拟时,震源所在断层尺寸采用Wells[16] (1994)等提出的经验公式计算
logS=-3.49 + 0.91MW(2)
logL=-2.44 + 0.59MW(3)
式中,S为断层面积;L为断层长度;MW为矩震级。
经过多次地震动模拟的探索,Beresnev[17]提出了子断层长度ΔL与震级之间的关系
logΔL=0.4MW - 2(4)
随机有限断层模型合成地震动时主要包含三种参数:震源参数、路径传播效应参数以及场地效应参数。
(1)震源参数
根据Brune[18]提出的震源谱模型

式中,M0是地震矩,ƒ为频率,f0动力拐角频率。此外,震源参数中还包含震源深度及应力降Δσ等。
(2)路径效应参数
路径效应参数主要包含路径品质因子Q[19]和几何扩散函数的形式,在数值模拟过程中,对加速度时程随震中距的传播产生影响。
(3)场地效应参数
场地效应参数包含高频消减参数Kappa[20],场地放大效应参数等,反映了局部场地对地震的影响。
根据随机有限断层法参数类型,结合马尼拉海沟俯冲带地质构造、地震动活动性的特点,表1设定了该俯冲带板缘地震参数。
表1 马尼拉海沟俯冲带板缘地震参数Table 1 Seismic Parameters of Plate Margin of Manila Trench subduction zone
在模拟马尼拉海沟俯冲带地震之前,为检验模拟效果,对实际板缘地震动不同台站的地震波形与相近地震参数下的模拟地震进行了对比,在此以日本东北部俯冲带板缘地震为例,在KiK-net,K-net获取2011年3月28日发生于该俯冲带震源深度为31 km的6.5级板缘地震MYG003台站数据,该台站震中距为95 km,最大加速度为133 gal,然后通过数值模拟方法合成发生于该俯冲带的震级6.5级板缘地震,震中位置及震源深度等数据与上述日本地震相同,比较两种数据的加速度时程及反应谱Sa,见图4。
据图4所示,虽然在强震动出现时间方面有所差异,但加速度时程的模拟结果与实际地震动在峰值范围及强震动持时方面比较接近,且模拟数据的最大加速度为125 gal,接近实际地震,因此模拟效果较好;两种形式地震动加速度反应谱的峰值范围相当,且在周期大于1.0 s以后,反应谱值趋于平稳,但模拟结果要略小与实际地震动,鉴于加速度峰值在地震动特点研究、工程应用等方面更有价值,加速度反应谱的模拟结果是可靠的。综上所述,日本东北部俯冲带利用随机有限断层法的模拟结果是合理的。
图4 日本东北部俯冲带加速度时程及Sa对比Fig.4 Comparison of acceleration time history and Sa of the subduction zone in northeastern Japan
随机有限断层法经日本东北部俯冲带验证可靠后,根据表1马尼拉海沟俯冲带板缘地震参数,进一步模拟了该俯冲带震级为5.5、6.5及7.5级的板缘地震,震源深度设置为30 km,加速度时程及反应谱见图5。
图5所示,马尼拉海沟俯冲带加速度时程中强震动出现在50~60 s区间内,且震级每增加一级,大震级加速度峰值为小震级的2.0~2.5倍,而震级变化并未改变加速度时程特点。在加速度反应谱图中,破坏性大的反应谱值主要在0~0.5 s,之后反应谱值趋于平稳(谱值>0),这一现象表明该俯冲带地震发生时,工程结构对地震波反应最为强烈的时间为0~0.5 s。
地震动衰减关系即地震动参数(PGA及Sa)随震级、距离(断层距或震中距)、震源深度及场地条件等因素变化的关系。在研究南海海域地震动衰减关系时,胡进军等[14]采用了赵兴权等[21]建立日本东北部俯冲带地震动衰减关系时的模型,经过南海海域板内地震动衰减关系建立过程的验证,本模型在描述地震动衰减规律时精确度高,适用性强,因此本文将该模型修改为适合板缘地震动的形式,见公式(6)
loge[ yi,j ( )T ]=aMW + bxi,j - log( xi,j + dexp( eMW) )+f (h - hc)+ SI + Sk + σ(6)
式中, y i, j ( )T 表示地震动参数,如PGA及S a等;MW为矩震级;xi,j为震中距;SI为板缘地震动参数;Sk表示场地系数,表示场地条件对衰减关系的影响;σ是标准差。
根据表1中马尼拉海沟俯冲带附近震源、场地及传播路径等地震参数合成地震动加速度时程后,利用公式(6)对数据进行随机效应回归,建立了该俯冲带PGA及各周期Sa的衰减关系,系数见表2,在这里,所模拟的地震震级范围为5.5~8.0级,震源深度为15~40 km。
获得马尼拉海沟俯冲带板缘地震动模拟衰减关系后,在无法利用实际地震数据来验证数值模拟所得板缘地震动衰减关系准确性的前提下,为提高模拟数据建立的地震动衰减关系的可靠性,本文采用胡进军等南海俯冲带板内地震动时衰减关系衍生方法的思路,建立马尼拉海沟俯冲带板缘地震动衰减关系。
图5 马尼拉海沟俯冲带加速度时程及Sa对比Fig.5 Comparison of acceleration time history and Sa of Manila Trench subduction zone
首先通过模拟地震数据建立日本东北部俯冲带的模拟衰减关系,并建立与马尼拉海沟俯冲带板缘模拟衰减关系之间的数量关系;然后以日本东北部俯冲带经验衰减关系为基础,衍生得到马尼拉海沟俯冲带板缘地震动衰减关系,其中,日本东北部俯冲带经验衰减关系为以日本东北部俯冲带板缘、板内地震动以及部分浅地壳的地震动记录为基础,通过衰减关系模型回归得到的包括板缘地震、板内地震及浅地壳地震在内的地震衰减关系系数。
表2 马尼拉海沟俯冲带板缘地震动模拟衰减关系系数Table 2 Simulated attenuation relation coefficient of ground motion at the plate edge of the Manila Trench subduction zone
以衰减关系的对数形式表示表示衍生过程,见公式(7)
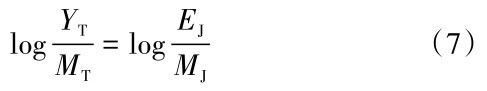
式中,EJ、MJ分别表示日本东北部俯冲带板缘地震动经验、模拟衰减关系;MT表示马尼拉海沟俯冲带地震动模拟衰减关系。对公式(7)数学变换,得到马尼拉海沟俯冲带板缘地震动衍生衰减关系为
logYT =logEJ +(logMT - logMJ)(8)
用公式(6)分别表示公式(8)中的logMT、logMJ及logEJ并合并同类项,最终马尼拉海沟俯冲带板缘地震衍生衰减关系表示形式为
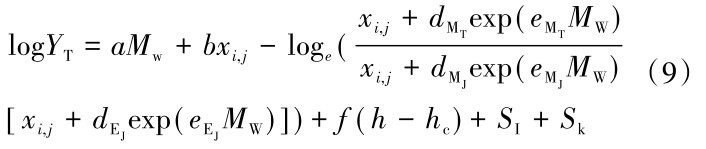
根据日本东北部俯冲带板缘地震动地震参数,采用随机有限断层法模拟了该俯冲带地震动加速度时程后,首先建立了该俯冲带的板缘地震动PGA及Sa的衰减关系,衰减关系系数见表3。
表3显示,PGA及各周期反应谱的衰减关系模拟结果,标准差均小于0.15,表明数值模拟板缘地震动加速度时程时设定的参数及回归得到的板缘地震动衰减关系比较合理;通过数值模拟方法建立日本东北部俯冲带板缘地震动模拟衰减关系之后,为进一步验证模拟结果的适用性,作出震级为5.0、6.0及7.0级时PGA以及周期分别为0.5 s, 1.0 s,2.0 s,3.0 s,5.0 s的Sa经验及模拟衰减关系曲线,见图6。
表3 日本东北部俯冲带板缘地震动模拟衰减关系系数Table 3 Simulated attenuation relation coefficient of ground motion in the subduction zone of northeast Japan
图6 日本东北部俯冲带经验与模拟衰减关系对比Fig.6 Comparison of the empirical attenuation relationship and the simulated one in the subduction zone of northeastern Japan
图6表示日本东北部俯冲带板缘地震动经验衰减关系与模拟衰减关系的PGA以及部分周期反应谱的对比结果。图中显示:①PGA以及短周期Sa的衰减关系中,采用数值模拟所得结果与经验衰减关系从量值及衰减规律的角度来看都比较接近,随着周期变大,二者间的差距会增大[22],但是经验衰减关系与所模拟的加速度数据仍然具有很强的相关性;②无论是PGA还是各周期Sa,模拟衰减关系的衰减速率在远场均大于经验衰减关系,造成此现象的原因主要是模拟情况下考虑的场地条件相对简单,而实际情况下场地条件比较复杂,对衰减的影响较大;③震级越大,两种类型衰减关系数值的差值会越大,这一现象表明随机有限断层法对中小震得模拟效果要优于大震。
表4 震级及距离综合项系数Table 4 Coefficient of magnitude and distance
在马尼拉海沟俯冲带板缘地震动模拟衰减关系以及与日本东北部俯冲带板缘地震动模拟衰减关系之间的数量关系建立之后,公式(9)所示衍生衰减关系建立过程中,震级、距离综合项所表示的形式较为复杂,且除该项之外,其他项在合并同类项时,均可通过系数作差来完成,而该震级、距离综合项是对数形式,作差运算不符合合并同类项规律,因此将该项进行以简化形式为目的的拟合,使形式更为简洁,该过程可以表示为公式(10),拟合结果见表4。
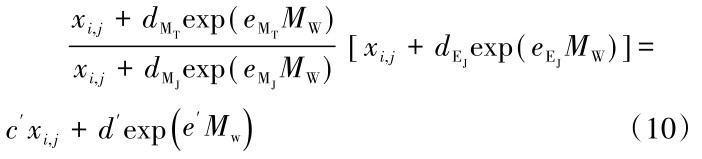
在表4中将震级、距离项通过回归分析简化后,马尼拉海沟俯冲带板缘地震动的衍生衰减关系也可以作相应的简化,见公式(11),最终衍生得到的马尼拉海沟俯冲带带板缘地震动衰减关系系数见表5。
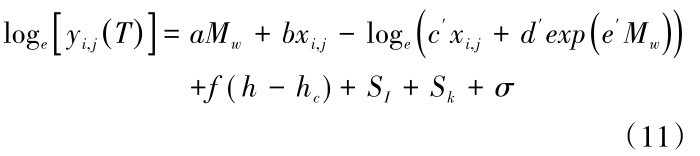
对于衰减关系的性质,主要关注随震级、震源深度的变化以及随震中距的衰减速率或趋势等特性,图7中作出了不同震级,震源深度为40 km时,马尼拉海沟板缘地震动PGA及部分周期反应谱衰减关系。
表5 马尼拉海沟俯冲带板缘地震动衍生衰减关系系数Table 5 Derivative attenuation coefficients of ground motions in the sbduction zone of the Manila Trench
据图7所示,PGA及短周期反应谱的模拟衰减关系与衍生衰减关系结果比较接近,但模拟衰减的PGA及反应谱随震中距的衰减速率要快于衍生衰减关系,并且随着震级增大,两种类型衰减关系PGA或反应谱等值点的震中距不断减小,这一现象表明,在短周期时,通过衍生方法得出的衰减关系更多考虑了场地条件、传播路径等因素,衰减关系更接近实际,但在短周期模拟衰减关系与衍生衰减关系差异较小,精确性可以满足要求;在长周期,两种方法所得的衰减关系差距较大,且模拟衰减关系所得的反应谱值更大,鉴于随机有限断层法模拟地震数据对短周期比长周期更有效的特点,在给定马尼拉海沟俯冲带板缘地震动衰减关系时,以衍生衰减关系为准。
图7 板缘地震动模拟与衍生衰减关系对比Fig.7 Comparison of simulated attenuation relationship and derived one of ground motion at the plate edge
本文以马尼拉海沟俯冲带为研究对象,分析了该俯冲带所在区域自1901年来历史破坏性地震的分布,并采用数值模拟方法合成了该俯冲带板缘地震,分析了地震特点,分别通过模拟数据及衍生方法建立了板缘地震动衰减关系,得到以下结论:
(1)俯冲带所在区域地震震中主要集中在马尼拉海沟及其东侧,多次发生震级大于7.0级的地震,破坏性很强,对南海海域的影响不容忽视;(2)在地震动加速度时程中,强震动主要集中在50~60 s左右,加速度反应谱中,0~0.5 s谱值较大,对建、构筑物影响较大;
(3)在PGA及短周期Sa的衰减关系中,衍生方法得出的衰减关系更多考虑了场地条件、传播路径等因素,衰减关系更接近实际,但模拟衰减关系与衍生衰减关系差异较小,精确性可以满足要求;在长周期,两种方法所得的衰减关系差距较大,且模拟衰减关系所得的反应谱值更大,鉴于随机有限断层法模拟地震数据对短周期比长周期更有效的特点,在给定马尼拉海沟俯冲带板缘地震动衰减关系时,以衍生衰减关系为准。